Chapter 13 Substitution Alpha to Carbonyl Groups
advertisement

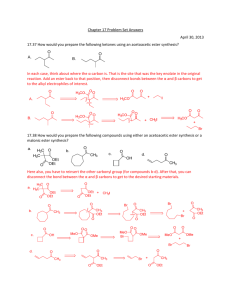
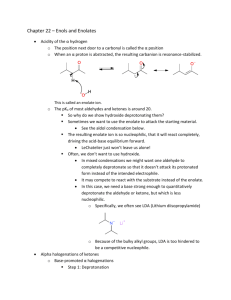
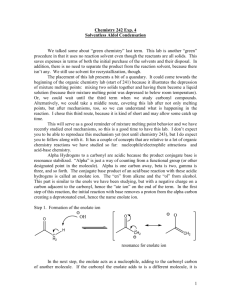
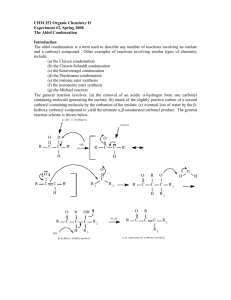
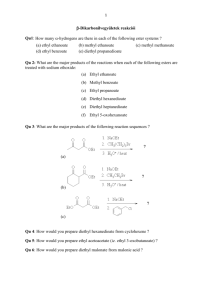
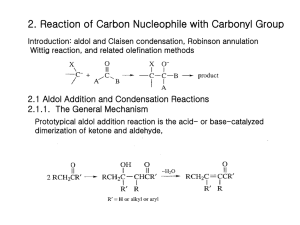
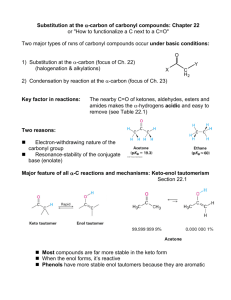
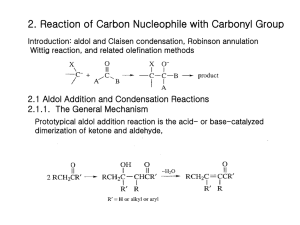
Chapter 13 Substitution Alpha to Carbonyl Groups • Formation and Reactions of Enolate Anions and Enols • Alkylation of Ketones and Esters: SN2 Reaction with Alkyl Halides • Aldol Reaction, Aldol Condensation and Related Reactions: Nucleophilic Addition of Enolate Anions to Carbonyl Groups • The Claisen Condensation and Related Reactions: Acylation of Esters • Alkylation of -Dicarbonyl Compounds • Synthetic Methods • Spectroscopy Chapter 13 Substitution Alpha to Carbonyl Groups • Formation and Reactions of Enolate Anions and Enols – – – – Molecular Orbitals of Enolate Anions Structure of Enolate Anions Protonation of Enolate Anions Halogenation Alpha to Carbonyl Groups • Iodoform Test – Kinetic versus Thermodynamic Deprotonation of Carbonyl Groups • Kinetic Control with Lithium diisopropyl amide (LDA) strong Base, poor Nucelophile Chapter 13 Substitution Alpha to Carbonyl Groups • Alkylation of Ketones and Esters: SN2 Reaction with Alkyl Halides – Works best with primary halide or secondary halide, but not tertiary – More later in the chapter with -ketocarbonyls Chapter 13 Substitution Alpha to Carbonyl Groups • Aldol Reaction, Aldol Condensation and Related Reactions: Nucleophilic Addition of Enolate Anions to Carbonyl Groups. – – – – – – The Aldol Reaction (typically at low [base]) The Aldol Condensation (at high [base] and high temp) Aldol Reaction and Aldol Condensation of Ketones Intramolecular Aldol Reaction and Aldol Condensation Crossed Aldol Reaction Nucleophilic Addition of ,-Unsaturated Carbonyl Groups: Conjugate Addition • Michael addition (Enolate reacts with ,-unsaturated carbonyl) • Robinson Annulation (two steps-Michael and Aldol condensation) • “Fun in Bases” Chapter 13 Substitution Alpha to Carbonyl Groups • The Claisen Condensation and Related Reactions: Acylation of Esters The Aldol Reaction – The Claisen Condensation • Enolate formation, addition, elimination, deprotonation, protonation • forms -ketoester – The Dieckmann Condensation • Cyclic Claisen used to form 5 & 6 membered rings • same 5 steps as Claisen – Crossed Claisen Condensation • Enolate anion reacts with ester or carbonate ester or oxalate ester or benzoate ester – The Reformatsky Reaction • Enolate anion formed from -halo carbonyl followed by addition to carbonyl and hydrolysis Chapter 13 Substitution Alpha to Carbonyl Groups • Alkylation of -Dicarbonyl Compounds -Dicarbonyl Compounds • highly acidic, resonance stabilized – Alkylation of -Ketoesters • via SN2 displacement, can form mono and disubstituted – Alkylation of Malonic Acid Diesters • similar to -Ketoesters – Hydrolysis and Decarboxylation of -Ketoesters and Malonic Acid Diesters • Ester hydrolyzed to carboxylic acid, heat to eliminate CO2 – Acetoacetic Ester and Malonic Ester Synthesis • Synthetic utility: first do mono- or disubstituted alkylation, then hydrolyze and decarboxylate to the more substituted ketone. – Formation of Carbocyclic Rings using the Acetoacetic Ester and Malonic Ester Syntheses • with di-bromo alkyl, can form carbocyclic ring via intramolecular closure Chapter 13 Substitution Alpha to Carbonyl Groups • Synthetic Methods – Review Table 13.1 p 692-693 • Using Enolate Anions and Enols to Introduce Various Functional Groups • Spectroscopy • Review of Reactions • Summary Chapter 13 Summary • Carbonyl enhances the acidity of hydrogen on -carbon • Treatment with base forms enolate anion, species with significant nucleophilic character • Under kinetic control conditions (e.g., LDA -Lithium diisopropyl amide) the less stable enolate forms • Under thermodynamic equilibrium conditions (e.g., with hydroxide) the more substituted enolate anion will form. • Enolate anions (and enols) are nucleophiles which react with electrophiles including halogen, alkyl halides, ketones, aldehydes and esters • Enolate intermediates in Aldol, Aldol condensation, Michael reaction, Robinson Annulation, Claisen and Dieckmann and Reformatsky reactions Chapter 13 Summary • Nucelophiles can add 1,2 or 1,4 to ,-unsaturated carbonyls – Grignard and alkyllithium reagents add 1,2 – Enolate anions add 1,4 • Aldol and Claisen are valuable synthetic tools for the construction of carbon-carbon bonds between carbonyl groups. • Dieckmann condensation and Robinson annulation form 5 and 6 membered rings intramolecularly. • Hydrolysis and Decarboxylation of corresponding acetoacetic and malonic diesters are useful synthetic steps for substituted ketones and carboxylic acids.