Naming Ionic Compounds
advertisement

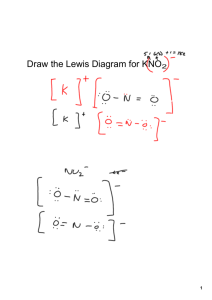
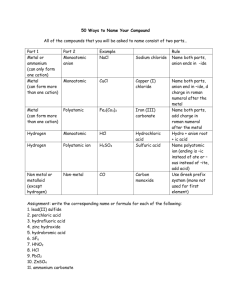
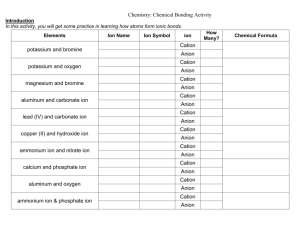
NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS Positively charged ions are called cations. Negatively charged ions are called anions. The cation is always named first. CATIONS: Cations can be metals or polyatomic ions. The ammonium ion (NH4+) is an example of a polyatomic cation. Hydrogen can also form a cation, H+, in which case the name hydrogen is used in naming. For metals having only one possible charge (valency) the name of the metal is used. Examples are Group 1 (1A) metals (charge +1), Group 2 (IIA) metals (charge 2+), aluminum (charge 3+), zinc (charge 2+), silver (charge 1+). For metals that can have more than one charge (valency) the name of the metal is followed by the valelncy in capital Roman numerals in brackets. Element Copper Copper Iron Iron Lead Lead Mercury Mercury Tin Tin Cation Cu+ Cu+2 Fe+2 Fe+3 Pb+2 PB+2 Hg+ Hg+2 Sn+2 Sn+4 Preferred Name Copper (I) Copper (II) Iron (II) Iron (III) Lead (II) Lead (IV) Mercury (I) Mercury (II) Tin (II) Tin (IV) ANIONS: Anions can be a negatively charged element or a polyatomic ion. Negatively charged elements can have the suffix –ide. Examples are oxide (O-2), sulfide (S2), fluoride (F-), chloride (Cl-), bromide (Br-), iodide (I-), nitride (N-), hydride (H-). A number of polyatomic anions exist, and these include: SO4-2 sulfate CO3-2 carbonate NO3- nitrate HCO3- hydrogen carbonate PO4-3 phosphate OH- hydroxide Compounds containing ions of elements: MgO Cation: magnesium Anion: oxide Magnesium oxide FeS Cation: iron (II) Anion: sulfide iron (II) sulfide LiH Cation: lithium Anion: hydride lithium hydride H2S Cation: Hydrogen Anion: sulfide hydrogen sulfide Compounds containing polyatomic ions: NaOH Cation: sodium Anion: hydroxide sodium hydroxide CaCO2 Cation: calcium Anion: carbonate calcium carbonate (NH4)2SO4 Cation: ammonium Anion: sulfate ammonium sulfate