Key terms - Mater Academy Lakes High School
advertisement

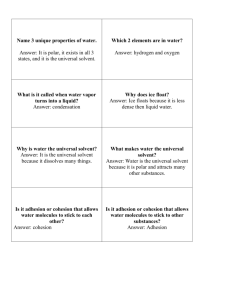
Chemistry Matter, Mass, Weight, &Density Elements & Pure Substances CHONPS – Elements of Life (Especially CHON) Atom: Nucleus & Electron Cloud (Composition & Charges) Subatomic Particles (Electrons; Neutrons; Protons) & Charges Protons & Physical Properties Neutrons: Their Role & Isotopes Electrons: Energy Levels & Chemical Properties Period Table Patterns (Reactivity; Size; Electronegativity; Metals vs. Non-Metals; Families; Periods) Scientific Use of Isotopes Compounds: Chemical Formula (Subscript & Coefficients) & Molecules Atom Electron Cloud Stability & Chemical Bonding: Ionic vs. Covalent (Single, Double, Triple) vs. Polar Covalent Intermolecular Attraction (Van der Wall Forces) Bioenergetics & Metabolism Energy in living systems Metabolism Kinetic vs. Potential Energy: General & in Biological Systems Energy & Work Energy & Matter Relationship Energy & Matter Conservation Energy Transfers & Entropy Energy & The States of Matter (Motion; Energy; Connection; Shape; Volume) Chemical Reactions: Chemical Equations; Reactants; Products; Arrows; Coefficients; Equilibrium; Bond Formation & Breakage Endergonic, Endothermic, Anabolic, Non-Spontaneous Reactions (i.e. Photosynthesis, Phosphorylation, & Dehydration Synthesis) vs. Exergonic, Exothermic, Catabolic, Spontaneous, Reactions (i.e. Cellular Respiration & Hydrolysis) Chemical Reaction Graphs (Products > Reactants vs. Products < Reactants) Chemical Bonds & Activation Energy Catalysis & Enzymes ATP Structure & Function Coupled Reactions & Biochemical Pathways Enzymes Enzyme (Quantity, Role, Reusable, Naming) Enzyme Structure (Protein; Active Site; Lock & Key; Induced Fit; Substrate Specificity; Structure & Function Link) Enzyme Mechanism: Activation Energy (Microenvironment; Participant; Orientation; Isolation) Enzymatic Action Factors: Environmental Conditions (ph, temperature, substrate concentration, enzyme concentration); Cofactors; Activators; Inhibitors (Competitive vs. Non-competitive) Allosteric Positive vs. Negative Feedback Mechanisms of Enzyme Control Water Formula & Structure Charge & Uneven Distribution Polarity Oxygen’s Electronegativity Hydrogen Bonding (Weak alone, but strong together) Melting / Boiling Points vs. Temperature & Pressure Major Properties & Hydrogen Bonds o Less Dense as a Solid (Crystal Lattice): Insulation & Floating o High Specific Heat (Resists Temperature Change): Maintaining Organism & Ecosystem Temperature o High Heat of Vaporization (Absorb Much Energy While Evaporating): Evaporative Cooling of Water; Organism Evapotranspiration Cooling; Greenhouse Effect o Cohesion (Stick Together): Surface Tension; Microhabitat for Organisms; Cell Tension; Capillary Action o Adhesion (Stick to Others): Leaf Water Conservation; Capillary Action; Universal Solvent o Solvent (Dissociation of Ions & Association to Polar Molecules): Chemical Medium for Life & Organization of Hydrophobic Molecules Mixtures o Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous o Solutions Solute & Solvent Aqueous & Tinctures Ions & Dissociation Other Soluble Molecules (Protein & Sugar Solubility) Electrolytes vs. Non-Electrolyte Solutions Hard vs. Soft water Effervescence Dissolving Rate (Stirring; Heating; Crushing) Solubility (CAN FIT) & Factors (Temperature; Type & Amount of Solvent) Concentration (IS IN): Dilute vs. Concentrated; Unsaturated, Saturated, vs. Supersaturated Freezing Point Depression & Boiling Point Elevation Polar vs. Non-Polar Interactions & Solubility (Hydrophobic, Insoluble, Non polar vs. Hydrophilic, Soluble, Polar) o Suspensions & Biological Examples o Colloids Acidity & Alkalinity o Water Dissociation & Hydroxide vs. Hydrogen (Hydronium) Ions o pH Scale: & Logarithms o Neutrality o Acids Facts: Common Ion, taste, reaction to indicators, pH range, examples o Bases Facts: Common Ion, taste, texture, reaction to indicators, pH range, examples o Neutralization Reaction & Salts o Precipitate & Precipitation Reactions o Buffers & Biological Function Biochemistry Carbon Based or Organic Molecules Elements of Life (CHONPS & HONC) Inorganic vs. Organic Compounds Carbon Chemistry: Bonds, Bond Shapes, and Molecular Structures (Rings, Pyramids, Chains) Hydrocarbons & Energy Functional Groups & Structure/Function Link o Hydroxide (Organic Alcohol) o Carboxyl (Organic Acid) o Amino (Organic Base) o Phosphate (Organic Charge) Macromolecules o Polymerization: Monomers Polymers through Dehydration Synthesis o Digestion: Polymers Monomers through Hydrolysis Carbohydrates TO BE CONTINUED….