The Molecules of Life Study Guide
advertisement

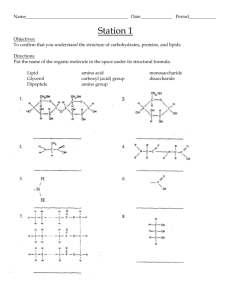
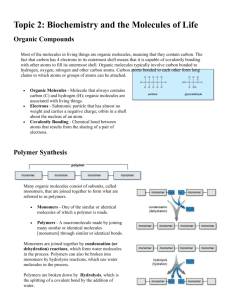
The Molecules of Life Study Guide Format: The questions on this test are designed to assess your knowledge of the meaning of key terms, your understanding of the major concepts we covered, and your ability to apply your understanding to solve problems. Consequently, you should expect to respond to a variety of question types, including multiple choice, sentence/table completion, interpretation of diagrams, and free response. Resources : You should be studying for this test using the notes you took on the slides covered in class, the reading and concept checks covered in the book, the skill practice worksheets, and the lab activities on molecular models, organic compounds in living things, and enzymes. Key Terms/Concepts: Organic Molecules Inorganic Molecules Hydrocarbons Functional Group Hydrophilic Monomers Polymers Dehydration Hydrolysis Carbohydrate Monosaccharide Disaccharide Polysaccharide Starch Cellulose Glycogen Lipid Hydrophobic Saturated Fat Unsaturated Fat Steroid Cholesterol Protein Amino Acid Polypeptide Peptide Bond Denaturation Activation Energy Catalyst Substrate Active Site Enzyme Essential Ideas: Aside from knowing the terms above, you should be able to: Identify an organic molecule given its structural formula Discuss the structure, function, and properties of the various types of organic molecules Describe the process of building and breaking polymers and be able to identify reactants and products in a chemical reaction. Discuss the role of enzymes in chemical reactions, including the process involved Review Questions: What is the difference between an organic molecule and an inorganic molecule? Provide examples of both organic and inorganic molecules. Compare and contrast monomers and polymers. Be able to identify monomers and polymers for carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. Which types of organic molecules are hydrophobic? Which types of organic molecules are hydrophilic? What are the products and reactants in a dehydration synthesis reaction? What are the products and reactants in a hydrolysis reaction? Describe a carbohydrate monomer and provide some examples. Describe a carbohydrate polymer and provide some examples. How do carbohydrates function in the body? How does the body store glucose? How is this different from plants? Describe a lipid monomer and provide some examples. Describe a lipid polymer and provide some examples. How do lipids function in the body? In what ways are steroids different from fats? Why is a steroid still considered a lipid? What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats? Describe a protein monomer and provide some examples. Describe a protein polymer and provide some examples. How do proteins function in the body? Which parts of amino acids are similar between all amino acids? And which parts are different? What is the relationship between an amino acid, polypeptide chain, and a protein? What does it mean when a protein is denatured? How might this happen? What is an enzyme and how does it function in the body? How does an enzyme interact with the substrate? Why is it a problem if an enzyme becomes denatured? What are two factors that might effect the functioning of an enzyme?