Earth Science Unit 6 Part 1 notes
advertisement
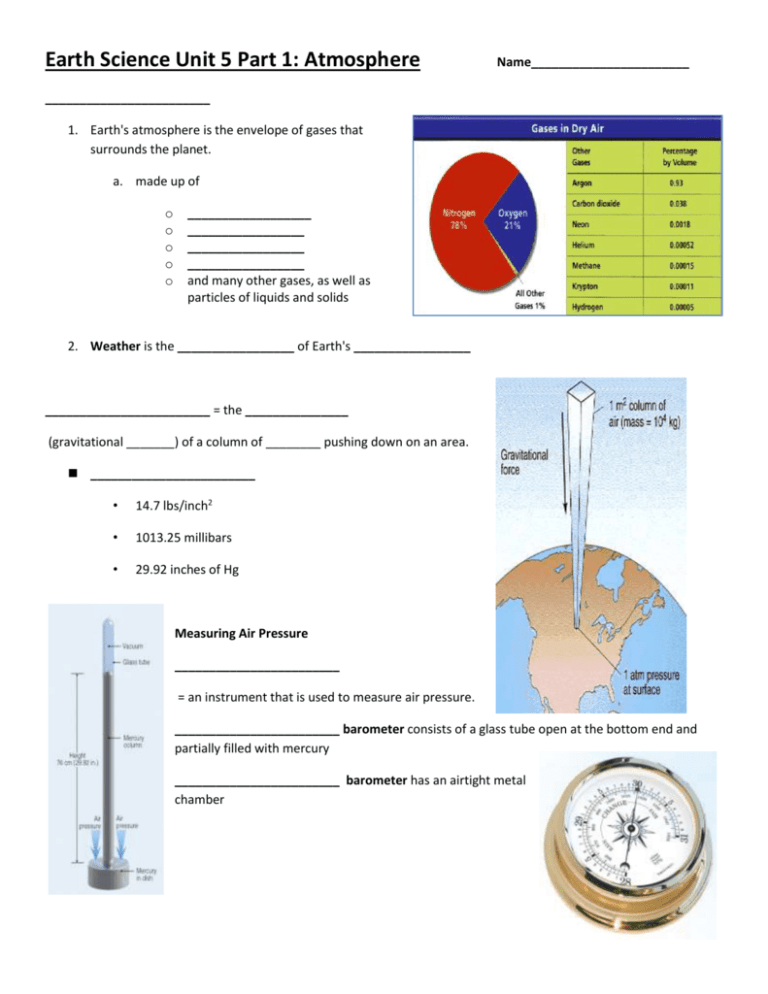
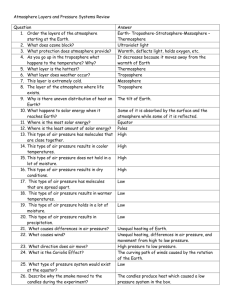
Earth Science Unit 5 Part 1: Atmosphere Name_______________________ ________________________ 1. Earth's atmosphere is the envelope of gases that surrounds the planet. a. made up of o o o o o __________________ _________________ _________________ _________________ and many other gases, as well as particles of liquids and solids 2. Weather is the _________________ of Earth's _________________ ________________________ = the _______________ (gravitational _______) of a column of ________ pushing down on an area. ________________________ • 14.7 lbs/inch2 • 1013.25 millibars • 29.92 inches of Hg Measuring Air Pressure ________________________ = an instrument that is used to measure air pressure. ________________________ barometer consists of a glass tube open at the bottom end and partially filled with mercury ________________________ barometer has an airtight metal chamber Air Pressure & Altitude 1. _______________= the distance above sea level. 2. As altitude _______________ Air pressure _______________ 3. As air _______________ decreases, so does _______________. Layers of the Atmosphere 1. Scientists divide Earth's atmosphere into four main layers classified according to changes in _______________. a. _______________ – sea level to 12 km i. All weather occurs here b. _______________ – from 12 to 50 km i. _______________ layer, ii. protects from _______________, iii. _______________ fly here c. _______________ – from 50 to 80 km i. Dense enough to burn _______________ d. _______________ – above 80 km, made up of 2 layers i. _______________– 80 km to 400 km 1. Gas particles electrically _______________ 2. Radio waves _______________ back to Earth from here 3. ______________________________occur here ii. _______________ – above 400 km 1. _______________ orbit here Energy in Earth's Atmosphere 1. Energy travels to Earth as electromagnetic _______________ from the _______________ 2. EMR travels through the atmosphere & _______________ the surface of the Earth 3. When Earth's surface is heated, it _______________ most of the energy back into the atmosphere as in_______________ radiation (Long wave radiation). Heat _______________in the Atmosphere 1. _______________ =the average thermal _______________ of the substance particles 2. _______________= transfer of thermal energy from a _______________object to a _______________ one Heat is transferred in 1 of 3 ways: a) _______________= heat given off b) _______________= heat traveling through soil c) _______________= hot (_______________) air masses rising, and cool (_______________) air masses falling _______________ 1. Wind is the movement of air from an area of high _______________ to an area of _______________pressure. 2. Winds are caused by _______________in air pressure caused by unequal _______________ of the atmosphere. Wind Direction / Wind Speed 1. Wind speed is measured with an _____________________________. 2. The name of a wind tells you the direction the wind is coming _______________. (eg, northwest) Local Winds Sea breezes & Land breezes are local winds caused by the unequal heating of Earth's surface Daytime: ______________________________ a) land _______________ up b) hot land air rises c) cool air from _______________ moves in to replace it. _______________: Land Breeze a) _______________ gives off heat gathered during day b) hot sea air _______________ c) _______________air from land moves in to replace it. ______________________________ Because Earth is _______________, global winds do not follow a straight path. 1. The way Earth's rotation makes winds _______________ is called the Coriolis Effect. 2. In the _______________ Hemisphere, global winds curve to the _______________. (clockwise) 3. In the _______________Hemisphere, global winds curve to the _______________. (counterclockwise) Global Winds occur over a large area & are affected by the Coriolis Effect (caused by the rotation of the Earth) 1. The Winds a. _______________ blow from the NE between Equator & 30N b. Prevailing _______________ blow from the SW between 30N & 60 N c. _______________Easterlies 60 N to 90 2. Calm Areas: a. _______________ along the equator b. The ______________________________around 30 N &S ______________________________= High speed wind currents about 150 mph that are 10-15 km above the surface The Water Cycle 1. _______________ : _______________ Label Me! 2. _______________: makes ___________ 3. _______________: Rain, snow, hail, etc. 4. _______________: over land (eg. _____) _______________ Earth Science Unit 5 Part 1: Atmosphere Name_______________________ Atmosphere 3. Earth's atmosphere is the envelope of gases that surrounds the planet. a. made up of o o o o o nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide water vapor, and many other gases, as well as particles of liquids and solids 4. Weather is the condition of Earth's atmosphere Air Pressure Air pressure = the weight (gravitational pull) of a column of air pushing down on an area. • 101.3 kPa (kilopascals) • 14.7 lbs/inch2 • 1013.25 millibars • 29.92 inches of Hg Measuring Air Pressure barometer = an instrument that is used to measure air pressure. mercury barometer consists of a glass tube open at the bottom end and partially filled with mercury aneroid barometer has an airtight metal chamber Air Pressure & Altitude 4. Elevation – the distance above sea level. 5. As altitude increases Air pressure decreases 6. As air pressure decreases, so does density. Layers of the Atmosphere 2. Scientists divide Earth's atmosphere into four main layers classified according to changes in temperature. a. Troposphere – sea level to 12 km i. All weather occurs here b. Stratosphere – from 12 to 50 km i. Ozone layer, ii. protects from UV, iii. jets fly here c. Mesosphere – from 50 to 80 km i. Dense enough to burn meteoroids d. Thermosphere – above 80 km, made up of 2 layers i. Ionosphere – 80 km to 400 km 1. Gas particles electrically charged 2. Radio waves reflect back to Earth from here 3. Aurora borealis occur here ii. Exosphere – above 400 km 1. Satellites orbit here Energy in Earth's Atmosphere 4. Energy travels to Earth as electromagnetic radiation from the Sun 5. EMR travels through the atmosphere & heats the surface of the Earth 6. When Earth's surface is heated, it radiates most of the energy back into the atmosphere as infrared radiation. Heat Transfer in the Atmosphere 3. Temperature =the average thermal energy of the substance particles 4. Heat= transfer of thermal energy from a hotter object to a cooler one Heat is transferred in 1 of 3 ways: d) Radiation= heat given off e) Conduction= heat traveling through soil f) Convection = hot (less dense) air masses rising cool (denser) air masses falling Winds 3. Wind is the movement of air from an area of high pressure to an area of lower pressure. 4. Winds are caused by differences in air pressure caused by unequal heating of the atmosphere Wind Direction / Wind Speed 3. Wind speed is measured with an anemometer. 4. The name of a wind tells you the direction the wind is coming from. (eg, northwest) Local Winds Sea breezes & Land breezes are local winds caused by the unequal heating of Earth's surface Daytime: Sea Breeze d) land warms up e) hot land air rises f) cool air from ocean moves in to replace it. Night: Land Breeze d) ocean gives off heat gathered during day e) hot sea air rises f) cool air from land moves in to replace it. Coriolis Effect Because Earth is rotating, global winds do not follow a straight path. 4. The way Earth's rotation makes winds curve is called the Coriolis Effect. 5. In the Northern Hemisphere, global winds curve to the right. (clockwise) 6. In the Southern Hemisphere, global winds curve to the left. (counterclockwise) Global Winds occur over a large area & are affected by the Coriolis Effect (caused by the rotation of the Earth) 3. The Winds a. Trade winds blow from the NE between Equator & 30N b. Prevailing Westerlies blow from the SW between 30N & 60 N c. Polar Easterlies 60 N to 90 4. Calm Areas: a. Doldrums along the equator b. The Horse Latitudes around 30 N & S Jet Stream= High speed wind currents about 150 mph that are 10-15 km above the surface The Water Cycle 1. Evaporation : -oceans and lakes Label Me! 2. Condensation: -makes clouds 3.Precipitation: -Rain snow hail, etc. 4. Runoff: -over land (eg. rivers) -groundwater