UNIT 4 - Atmosphere Vocabulary PART 1
advertisement

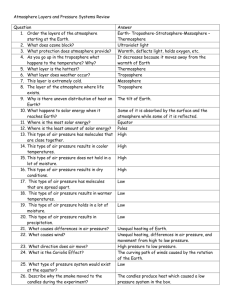
UNIT 4 - Atmosphere Vocabulary PART 1 Storm surge – abnormal rise of the sea along a shore as a result of strong winds local winds – winds causes by either topographic effects or by variations in surface composition (land and water) in the immediate area cyclones – low-pressure center characterized by a counterclockwise flow of air in the Northern Hemisphere wind – movement of air from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure Coriolis Effect – apparent deflective force of Earth’s rotation on all free-moving objects, including the atmosphere and oceans; to the right in the Northern Hemisphere dew point – temperature to which air has to be cooled in order to reach saturation front – the boundary between two adjoining air masses having contrasting characteristics heat – thermal energy transferred from one object to another monsoons – seasonal reversal of wind direction associated with large continents, especially Asia; winter = wind from land to sea, summer = wind from sea to land rotation – spinning of a body, such as Earth, about its axis (day) revolution – the motion of one body about another, such as the Earth moving in its orbit about the Sun (year) latent heat – energy absorbed or released during a change in state temperature – measure of the average kinetic energy of individual atoms or molecules in a substance weather – the state of the atmosphere at any given time and place absorption – interception of radiant energy by objects, such as Earth’s atmosphere anticyclones – high-pressure center characterized by a clockwise flow of air in the Northern Hemisphere climate – observations of weather collected over many years that help describe a place or region orographic lifting – pushing up of air by elevated terrain (such as mountains) relative humidity – ratio of the actual amount of water vapor in a parcel of air compared to the amount of water vapor it can actually hold stratosphere – about 12km to 50km above Earth’s surface; temperature increases as you go higher (due to ozone layer); ozone layer is found here troposphere – from Earth’s surface up to about 12km; temperature decreases as you go higher; layer where most weather events occur exosphere – most outer layer of Earth’s atmosphere; mixed layer between Earth’s atmosphere and space thermosphere – about 85km to 100km above Earth’s surface; temperature increases as you go higher (due to solar radiation) mesosphere – about 50km to 85km above Earth’s surface; temperature decreases as you go higher PART 2 air pressure - exerted in all directions, when the air pressure pushing down on an object exactly balances the air pressure pushing up on the object barometer - a device used for measuring air pressure pressure gradient - the spacing of isobars that shows the pressure changing occurring over a given distance jet streams – fast moving rivers of air at high altitudes trade winds - two belts of winds that blow almost constantly from easterly directions polar easterlies - winds that blow from the polar high toward the subpolar low polar front - the interaction of these warm and cool air masses westerlies - air traveling towards the poles prevailing wind - when the wind consistently blows more often from one direction than from any other; from west to east in the continental United States anemometer – instrument commonly used to measure wind speed El Nino - episodes of ocean warming that affect the eastern tropical Pacific; causes dry areas to receive more rain than usual and wet areas to be dryer than usual; often occurs in 7 to 10 year cycles PART 3 air mass - an immense body of air that is characterized by similar temperatures and amounts of moisture at any given altitude warm front - forms when warm air moves into an area formerly covered by cooler air cold front - forms when cold, dense air moves into a region occupied by warmer air stationary front – occurs when air flow is almost parallel to the line of the front occluded front – occurs when an active cold front overtakes a warm front thunderstorm – a storm that generates lightning and thunder; frequently produce gusty winds, heavy rain, and hail tornado – a violent windstorm that takes the form of a rotation column of air called a vortex which extends downward from a cumulonimbus cloud hurricane – a whirling tropical cyclone with winds of at least 119kph; occur most often in late summer global warming – an increase of global temperatures due to increased levels of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases