air pressure
advertisement

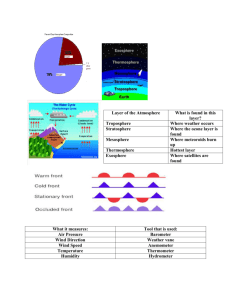
Ch 6 Study Guide Part I – Identify – Possible multiple choice topics Percentage of Oxygen, Nitrogen in atmosphere – 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen global wind patterns - are an example of the atmosphere acting as a system Density – amount of mass per volume of a substance Barometer – measures air pressure Mercury barometer – measures air pressure using liquid mercury aneroid barometer – measures air pressure without using a liquid Barometer differences – aneroid = no liquid, mercury barometer uses liquid air pressure - is the result of the weight of a column of air pushing down on an area. Air pressure and density differences at high altitudes – air pressure and density decrease as you rise in elevation Differences between warm and cool air – warm air is less dense and will rise in the atmosphere; cool air is more dense and sinks in the atmosphere layers of the atmosphere – troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere. Ordered by temperature differences Greenhouse effect - the process by which gases hold heat in the atmosphere. local winds – winds occurring over small differences. Ex. Sea Breezes and Land Breezes Global winds – winds occurring due to atmospheric convection currents. Ex. Prevailing Westerlies (here), Trade winds, etc. Differences between local and global winds - Local winds differ from global winds because they are caused by unequal heating within a small area. Coriolis Effect – when the Earth’s rotation makes global winds curve. Temperature differences in layers of the atmosphere - layers of the atmosphere are order/determined by temperature differences Types of electromagnetic radiation – pg 239 chart Ozone – form of oxygen with three atoms. In the stratosphere, it forms a layer which protects the Earth from Ultraviolet rays causes of winds – differences in air pressure due to uneven heating of the earth Temperature – average amount of energy of motion of each particular in a substance Thermometer - is used to measure how hot or cold the air is. Celsius Scale – temperature scale where 0° is freezing point of water and 100° is the boiling point of water Conduction – transfer of heat energy between objects that are touching Convection – transfer of heat energy in a fluid. Radiation – transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves Main global wind affecting North America Ch 6 Vocabulary Words Part II –Short Answers 1. Contrast the three ways in which heat is transferred. Radiation is the direct transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves. Conduction is the direct transfer of heat between substances that are touching. Convection is the transfer of heat by the movement of a fluid. 2. Explain why military aircraft pilots must wear masks that provide oxygen when they fly at high altitudes. As you move higher in the atmosphere, air pressure decreases. As air pressure decreases, so does air density. Less-dense air has fewer oxygen molecules to breathe per cubic meter, so pilots breathing this less-dense air need additional oxygen to survive. 3. Describe three ways that the atmosphere helps living things survive on Earth. Include information in your answer about the characteristics of the different layers. The ozone layer in the stratosphere protects living things from dangerous radiation from the sun; it traps energy from the sun to keep Earth’s surface warm enough for living things to survive; the mesosphere prevents Earth’s surface from being hit by most meteoroids 4. Explain why the region near the equator has little or no wind. Near the equator, the sun is strong and constantly heats the air. The warm air expands, rises steadily, and creates an area of low pressure. Cool air moves into the area, but it is warmed rapidly and rises before it moves very far. Little or no wind occurs because the air does not move horizontally.