Meteorology Study Guide
advertisement

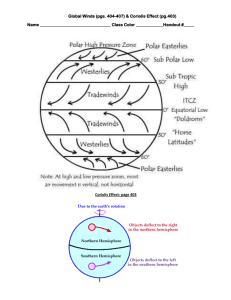
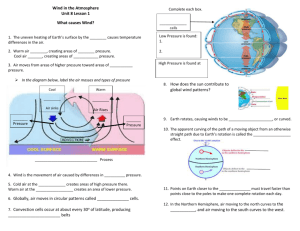
Meteorology Study Guide 1.When Earth’s axis is tilted so that the North Pole is more directly facing the sun, what season is South America experiencing? 2. Earth’s axis tilts at an angle of approximately 23.5°. If Earth’s tilt were reduced to zero, how would the seasons on Earth be affected? 3. Daylight in the northern hemisphere last longer in the summer then in the winter and the change in the length of day happens in a predictable pattern. Which statement correctly explains this condition of Earth’s environment? 4. What is the result of the tilt of Earth’s axis? 5. Day and night are caused by ___________________________________ 6. The length of a year is determined by Earth’s ________________________________. 7. The atmosphere is _______________________________________________________________________________________________. 8. The 2 most abundant gases in the Earth’s atmosphere are __________________________ and ______________________. 9. Instruments that are used to measure air pressure are called _______________________________. 10. As you rise farther in the atmosphere, air pressure _____________________________________. 11. When climbing a high mountain, you get out of breathe easily because ____________________________________. 12. Why is air pressure greatest at the Earth’s surface? 13. The condition of the Earth’s atmosphere at a particular time and place is known as ________________. 14. The map below shows the locations of low-pressure and high-pressure belts across North and South America. Why is pressure low at the equator relative to pressure at 30°N or 30°S latitude? 15. What factors affect the temperature of precipitation such that snow falls in the winter and rain falls in the summer? 16. Wind occurs because of differences in _____________________________. 17. What causes the air pressure differences that cause winds? 18. The winds that blow from 30O latitude in both hemispheres toward the equator are called _____________ 19. The winds that blow from 30o to 60o latitude in both hemispheres are called _______________________. 20. The winds that blow from the poles to 60o latitude in both hemispheres care called ____________________. 21. Why does most of the rain for Georgia come from Alabama to our west? 22. What causes local winds? 23. At the seashore late in the afternoon on a hot sunny day, a person often feels a strong breeze coming in from the ocean. Which of the following is the reason for the breeze? 24. What type of wind is being described? Warm air above the ocean rises and cooler air above the beach moves to take its place. 25. An air mass gets its temperature and humidity from ______________________________. 26. Cold air masses that form at high latitudes are called ____________________________ 27. An air mass forms over the Gulf of Mexico and moves northeast across Georgia. What weather conditions are likely to prevail in Georgia? 28. If the meteorologist describes an arctic, dry air mass. What type of air mass is he describing? Match the labels to the map. Write the letters in the space provided. Source Regions for Air Masses That Influence Weather in North America _____ 29. mP _____ 31. mT _____ 30. cP _____ 32. cT 33. What kind of weather does a stationary front bring? Use the Diagram to answer the following questions (34-35). 34. The diagram above represents the meeting of two air masses. The air mass on the left is formed over a polar region and the air mass on the right formed over the tropical region. Which type of front is pictured in the diagram? 35. What kind of weather is associated with this type of front? 36. What type of clouds usually indicates a change in weather? 37. Which type of cloud could be in the sky if the weather is sunny? 38. On a July day large cumulonimbus clouds are forming. It is very warm and humid and the barometer is falling. What kind of weather could you predict? 39. If there is a tornado warning in your area, you should ______________________________. 40. Under what conditions is a hurricane most likely to form?