Unit 8 Vocabulary
advertisement

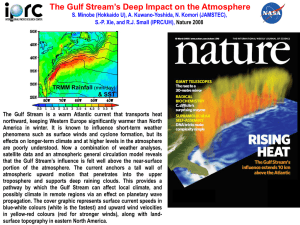
Unit 8 Vocabulary Climatic Interactions hurricane - a huge, slowly-spinning tropical storm that forms over water and has winds of at least 119 km/h (74 mph). upwelling – subsurface ocean current that brings nutrient-rich water from the ocean bottom to the surface. convection current – when temperature differences cause fluids to expand and move; the less dense areas continually rise, and the more dense areas continually sink creating a cyclical current. atmosphere – an envelope of mixed gases are held to the Earth by gravity; the densest gases are near the surface of the Earth. cyclone – a storm or system of winds that rotates about a center of low atmospheric pressure counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere, advances at a speed of 20 to 30 miles (30 to 50 kilometers) an hour, and often brings a great deal of rain. jet stream – narrow stream of high-speed wind in the atmosphere, generally moving west to east in the Northern Hemisphere. gyres – a circular or spiral motion or form; a giant circular oceanic surface current. Gulf Stream – warm current in the North Atlantic flowing from the Gulf of Mexico northeast along the United States coast to Nantucket & then eastward. humidity – amount of water vapor in the air. psychrometer – instrument used to measure moisture in the atmosphere. prevailing winds – mid-latitude global wind that blows mostly in one direction. air mass – a large body of air that has about the same temperature and humidity throughout it. air pressure – a measure of the weight of the atmosphere per unit of area on the Earth’s surface; also called barometric pressure. deep water currents – movement of deep water in the ocean basins by density driven forces and gravity; the density difference is a function of different temperatures and salinity. surface currents – ocean current flowing at the surface, caused mainly by winds. anemometer – instrument used to measure wind speed. weather front – a boundary separating two masses of air of different densities, and is the principal cause of meteorological phenomena.