Carboxylic Acids and Esters
advertisement
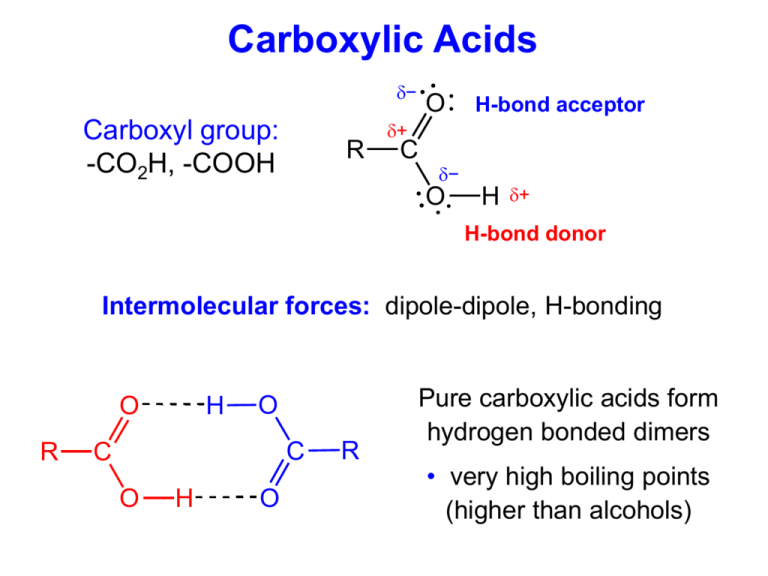
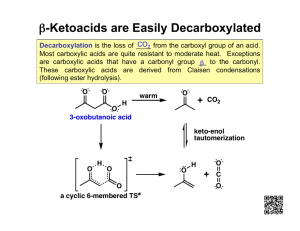
Carboxylic Acids − Carboxyl group: -CO2H, -COOH R O H-bond acceptor + C − O H + H-bond donor Intermolecular forces: dipole-dipole, H-bonding O R H O C C O H O R Pure carboxylic acids form hydrogen bonded dimers • very high boiling points (higher than alcohols) Carboxylic Acid Nomenclature O R C • Parent chain: longest containing carboxyl group (COOH) O H • Name of parent: replace “–e” with “–oic acid” • Numbering starts at carboxyl carbon – Priority: Carboxylic acid > aldehydes > ketones > alcohols O O “hydroxy” “oxo” substituent substituents OH 3-oxobutanoic acid O (diabetes) O HO O OH OH propanedioic acid (apples) trans-3-methyl-2-hexenoic acid (human armpits) OH O O OH O HN O CH3 aspirin Tylenol Can irritate your stomach Gentle on the stomach A carboxylic acid Just an alcohol Carboxylic Acid Reactions • Acid-Base reactions (formation of carboxylate salts) O O R + C R NaOH OH + C O carboxylic acid + strong base H2O Na carboxylate salt + water Naming: cation, then anion (regular ionic compound) Anion name: replace “–oic acid” with “–oate” O sodium hexanoate O Na • Reduction to 1° alcohols – Only LiAlH4 reduces carboxylic acids (not NaBH4 or H2/Pt) O LiAlH4 butanoic acid OH 1-butanol OH What are the products? O O OH 3-oxo-4-pentenoic acid H2/Pt NaBH4 LiAlH4 OH O OH OH O OH 3-hydroxypentanoic acid 3-hydroxy-4-pentenoic acid OH OH 4-pentene-1,3-diol Carboxylic Acid Reactions • Certain molecules can attack the carboxyl carbon and replace the –OH group O O R C + H H−Nu OH R C + H2O Nu H−Nu Product O H-OR′ Alcohol Ester R C OR' O H-NH2 Amine Amide R C NH2 What do these flavors/smells have in common? O O O O apricot O O O grape pear rum O O O O H O NH2 O banana O O O O O apple orange O O raspberry OH pineapple wintergreen O Made from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol R Esters C O R' Esters from Carboxylic Acids & Alcohols • Nucleophilic substitution – a condensation reaction O R O H+ C + O H carboxylic acid O R' R C O H + + alcohol H 2O R' + ester water • Reverse reaction = hydrolysis (“water-splitting”) O R C + O ester O H+ H 2O R' + R C + O water H carboxylic acid O R' H + alcohol Esters O O R – C – O – R’ O H H O H C C C O CH H 3 from propanoic acid methyl group H H an ester a carboxylic acid propanoic acid An ester is similar to a carboxylic acid, but the acidic hydrogen has been replaced by an alkyl group (R) methyl propanoate Naming Esters • Named as “alkyl alkanoates” – Alkyl group first (from alcohol) – Acid name: “-oic acid” changed to “-oate” O ethyl butanoate O (pineapple) O pentyl butanoate O (apricot) O 1 O 3-methylbutyl ethanoate 3 2 4 (banana) Naming Esters O O O R – C – O – R’ Name the following ester: O CH3CH2CH2C-O-CH2CH3 Step 1) the ester alkyl group (R’) = ethyl Step 2) the acid (R) = butanoic acid Step 3) the name = ethyl butanoate Formation of an Ester H H H O H C C C C O OH H + H H H butyric acid (butanoic acid) H H HO C C H H H ethyl alcohol + water ethyl butanoate or ethyl butyrate (tastes and smells like pineapple) D O Ester CH3 O H C O C CH3 Raspberry R C O R' H H O CH3 H C C O CH2 CH2 CH CH3 H CH3 Banana H O H C C O CH2 (CH2)6 CH3 H Orange Ester H O O H C C O CH2 CH2 CH3 H R C O R' Pear H H C H O C H C C O CH2 C H Peach C H C H C H Structural Isomers • Draw all possible isomers of C3H6O2 Two oxygen's → carboxylic acids and esters