Stress, Faults, & Mountain Building Name: Earth Science Notes
advertisement

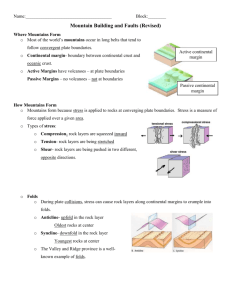
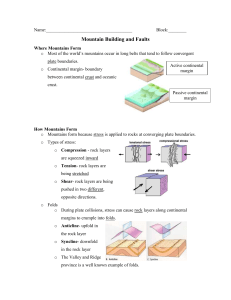
Stress, Faults, & Mountain Building Earth Science Notes- Ms. Blessing Name: Block: Date: Where Mountains Form (pp. 236-237) A is a large mass of rock that rises a great distance above its base. Most mountains occur in long belts along A plate boundaries. is a boundary between oceanic and continental crust. There are two types: 1. occur along plate boundaries (ex: West coast of US and South America) What has accumulated along the passive continental margin of the Eastern United States? 2. Where did it come from? do not occur along plate boundaries (ex: East coast of US) How Mountains Form (pp. 238-241) is a measure of force applied over a given area. Rocks at the surface of the Earth usually respond to stress by , while stress applied to rocks within the surface of the Earth may cause the rocks to or . 3 different types of STRESS: Type of Stress 1. Compression 2. Tension 3. Shear What is it doing to the rocks? Result of stress Picture (use arrows) What type of plate boundary? (THINK!) During plate collisions, stress can cause rock layers along continental margins to crumple into . (picture bottom left) An up fold in the rocks is called an (looks like an ‘A’)- label below A down fold in the rocks is called a (looks like a dip)- label below FAULTS (write definition) - The part of the fault above the fault plane (picture top right) is called the wall and the part of the fault below the fault plane is called the wall. Q. How do geologists classify faults? - 4 types of FAULTS: Type of Fault What happens? Picture (Use arrows) What type of plate boundary? (THINK!) 1. Normal Fault 2. Reverse Fault 3. Thrust Fault 4. Strike-Slip Fault (Transform Fault) - , like faults, are breaks in the bedrock along which no movement has occurred. Joints provide channels through which fluids enter and move through rock. Types of Mountains (pp. 243-245) Type of Mountain How is it formed? Type of Stress Picture (from above) (draw the mountains!) Plate Boundary & Location on Earth’s Surface 1. Folded 2. Dome 3. Volcanic 4. Fault-Block (Horsts & Grabens) Analysis & Summary Questions (Based upon what you learned and already know about plate tectonic boundaries!) 1. How are plate boundaries related to stress and faulting? 2. How is stress at plate boundaries related to the formation of metamorphic rocks? 3. Compare and contrast a fault and a joint. 4. In general, where do we find mountains? Why are some mountains found along areas where there is no plate boundary? (Think of Continental Drift!)