MOVEMENTOFTHEEARTHSCRUST
advertisement
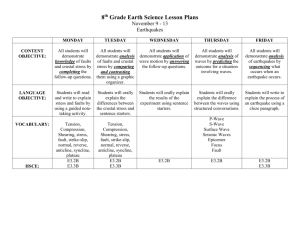
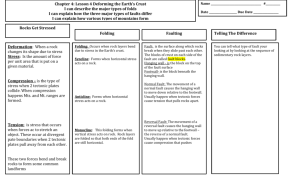
MOVEMENT OF THE EARTH’S CRUST Earth’s crust can be deformed through: Faulting Folding Uplifting How does the crust change it’s shape over time? • As rocks undergo stress (push-pull force) they slowly change SHAPE and VOLUME Stress causes breaking, tilting and folding ►DEFORMATION 3 Types of Deformation 1. Compression - squeezes rocks together causing crustal rocks to be pushed higher and deeper. 2. Tension – pulls rocks apart causing crustal rocks to be thinner in the middle than at the ends. 3. Shearing – pushes rocks horizontally in two directions. FAULTS - a break or crack along which rocks move • Hanging Wall – block of rocks above the fault. • Foot Wall – block of rocks below the fault. Types of Faults • Normal Fault : tension causes the hanging wall to move down relative to the foot wall. • Reverse Fault : compression causes the hanging wall to move up relative to the foot wall. • Strike – Slip Fault : shearing causes the blocks of rock to move horizontally past one another. Types Normal Fault Reverse Fault Strike-slip Fault Fault Block Mountains • Many Normal Faults in one area may create mountains & valleys. • Mountains formed by blocks of rock uplifted are called fault-block mountains. Ex : Grand Tetons, WY Fold – a bend in a rock • Sometimes when stress is applied to crustal rocks, they bend but do not break • Anticline – upward fold • Syncline – downward fold Normal Faults Reverse Fault Strike-Slip Faults Folds & Faults