EARTH SCIENCE MID-TERM STUDY GUIDE `11
advertisement

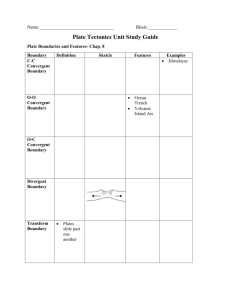
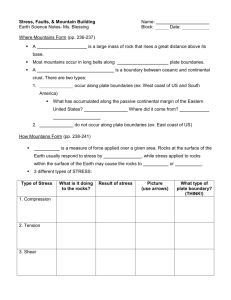
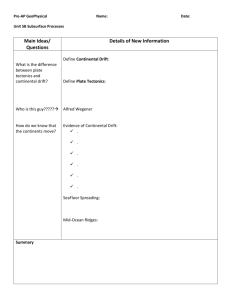
EARTH SCIENCE MID-TERM STUDY GUIDE ’11-‘12 Name: Date: This midterm covers the following topics & chapters in your textbook: 1. Scientific Investigations (Ch. 1 & 2) 2. Mapping (Ch. 3) 3. Earth’s formation/composition (Ch. 4) 4. Plate Tectonics & Mountain Building (Ch.’s 8, 10, & 11) 1. Define or describe the following words: (They may not all be in the glossary!!!) a. model b. closed system c. open system d. atmosphere e. biosphere f. geosphere/lithosphere g. hydrosphere h. cycle i. process j. albedo k. geothermal energy l. tidal energy m. solar energy n. carbon cycle o. water cycle p. hypothesis q. evidence r. scientific method s. law t. theory u. technology v. map projection Mercator projection Polyconic projection Gnomonic projection w. equator x. prime meridian y. tropic of cancer z. tropic of Capricorn aa. plane-table surveying bb. map scale graphical/bar scale verbal scale fractional/ratio cc. Global Positioning System (GPS) dd. contour line ee. contour interval ff. latitude gg. longitude Block: hh. condensation ii. evaporation jj. precipitation kk. plate boundaries convergent boundary divergent boundary transform boundary ll. hot spot mm. earthquake nn. travel-time graph oo. epicenter pp. focus qq. seismic wave p-wave s-wave l-wave rr. seismograph ss. seismogram tt. fault normal fault reverse fault thrust fault strike-slip/transform fault uu. Richter Scale vv. magnitude ww. sonar xx. map profile yy. conduction zz. convection aaa. radiation bbb. continental margin active passive ccc. density ddd. mass eee. volume fff. convection cell/current ggg. layers of the earth hhh. Theory of Continental Drift iii. Theory of Plate Tectonics jjj. stress shear tension compression 2. What are the units of latitude and longitude and how are coordinates written to describe a location on the surface of the Earth? -degress, minutes, seconds 3. What is the difference between open and closed systems? NRG can exchange in an open system but not in a closed system 4. Name the four spheres of the earth system and list examples for each sphere. geosphere-rocks atmosphere- layer of gases hydrosphere – all H 0 biosphere – all life 5. Where is most of earth’s fresh water located? glaciers 6. Where is most of the earth’s water located? oceans 7. The Carbon Cycle is a biogeochemical cycle. Describe how carbon is passed from one sphere to the next. Photosynthesis, volcanoes, burning fossil fuels 8. Where does the majority of Earth’s energy come from? solar 9. What would happen if the Earth took in more energy than it released? Get warmer 10. List surfaces on the earth that would have a HIGH albedo. Oceans, lakes, snow fields 11. Where does the earth’s tidal energy come from? Moon’s gravity 12. What is the goal of science? To understand the natural world 13. How do scientists test their ideas? experiments 14. What do depression contours show (i.e. what is a depression)? Holes, craters, etc. 15. Draw a depression contour. 16. What does it mean when many contour lines are close together? Steep slope / cliff 17. Describe the “Rule of V’s” as it relates to rivers on topographic maps. V’s point upstream / source 18. Look at the topographic map to the right. a. In which direction are the v’s pointing? E b. Which direction is the river flowing? W 19. What tools are needed to make a topographic map profile? Paper and pencil 20. How many time zones are there in the world? 24 21. How do travelers going west across the International Date Line change their calendars? Gain 1 day 22. Where are you if your longitude is 0°? Prime Meridian 23. What types of technology do scientists use to create maps today? Satellites, airplanes, computers, photos 24. What is Earth’s original surface thought to have been made of? Craters like the moon 25. Earth’s imperfect shape is the result of what? rotation 26. Why does an object weigh less at the Equator than at the poles? Because the Earth is not a perfect sphere 27. List the initial sources of Earth’s heat when it was first formed. Radioactive, collision with other materials 28. What is the composition of Earth’s inner core? Solid Fe & Ni 29. What type of plate boundary does new ocean and volcanoes occur at? Diversing / spreading 30. What will ultimately happen to all of our glaciers if humans keep burning fossil fuels for energy? melt 31. How many seismograph stations are needed to locate the epicenter of an earthquake? 3 32. Look at the travel-time graph to the right. a. What is the arrival time of the first p-wave if the distance from the epicenter is 1000 miles? 3.2 secs (3) b. What is the arrival time of the first s-wave if the distance from the epicenter is 1000 miles? 7.2 secs (7) c. What is the difference in arrival times of p and s waves if the distance from the epicenter is 1000 miles? 4 secs 33. What two gases make up 99% of the Earth’s atmosphere? 0 N 34. What type of mountains form at subduction zones? volcanic 35. What type of continental margin do mountains occur along? collision 36. Describe and draw a convection cell. 37. Who was the scientist to come up with the theory of continental drift? Alfred Wegner 38. Where do the majority of earthquakes and volcanoes occur? Plate boundaries 39. Describe the “Ring of Fire”. Pacific Ocean basin subduction zones 40. What is the formula for density? d=m/v 41. What are the units for density? Grams / cm 42. How do you measure the density of an irregular object? Describe this method. Water displacement 43. What is the volume of this cube? 8cm 44. If the mass of this cube is 36g, what is its density? 2cm 4.5 grams / cm 45. Base your answers to the following questions on the diagrams below. Objects A and B are made of the same uniform material. a. If Object B has a mass of 173g, what is its density? b. What is the density of Object A? 4 cm Object A Object B 4 cm 4 cm 46. What is the time difference between point A and point B? 5 hours behind 47. Which point is ahead of the other point? A 48. If it is 12 noon at point B, then what time is it at point A? 5pm B A 49. What is the location of Shanghai, China? 31 5`N, 122 0`E 50. What is the location of Tokyo, Japan? 35 2`0” N, 139 0`0” E 51. What type of plate boundary does each of the following letters represent? (Be specific!) a. Hawaii – hot spots b. Los Angeles, CA - transform c. West coast of South America- subduction d. Iceland – on a spreading / diverging boundry e. East Africa – rift valley / diverging f. Northern India – colliding / converging 52. Trace the border of the “Ring of Fire”. 53. How many centimeters are in a meter? 100cm 54. How many millimeters are in a centimeter? 10mm=1cm 55. What are the units for mass and volume? Liter, milliliter, gram, kilogram