Review Guide for Test 3 – Plate Tectonics Vocabulary words you
advertisement
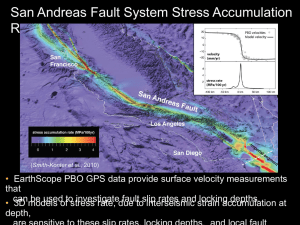
Review Guide for Test 3 – Plate Tectonics Vocabulary words you should be familiar with for this unit: Normal fault Crust Mantle Inner Core Reverse fault Continental Plate Ocean Plate P-wave Strike-slip fault Lithosphere Asthenosphere Alfred Wegener Pangaea Mantle convection Divergent Convergent Strike-slip Rift Ridge Trench Hot spot Ring of fire Stratovolcano Cinder cone Vol. Compression stress Mt. St. Helens Viscosity Fire fountain Plinian Shear stress Pyroclastic flow Aa lava Tension stress Anticline Nebula hypothesis Epicenter Fault Syncline Richter magnitude Tsunami Seismogram Seismograph(mometer) S-P Graph Pahoehoe lava Outer Core S-wave Continental Drift Transform boundary Mountain Shield Volcano Effusive Plume Focus Aftershock Caldera Key concepts and skills to master: o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o Names/locations of major and minor tectonic plates Interior of the Earth / Layers of the earth and their properties Relationship between lithosphere and asthenosphere How mantle convection drives plate tectonics Contributions of Alfred Wegener His evidence / problems / Pangaea Divergent boundaries Types of / Real-life examples of / Features of Convergent boundaries Types of / Real-life examples of / Features of Transform boundaries: Types of / Real-life examples of / Features of Hot spots & How Hawaii formed Major mountain ranges of the world Hawaii vs. Iceland Earthquake risk in the United States Volcano types, properties, eruptions, and examples of each type Volcanic activity in the solar system Mount St. Helens before and after How to locate the epicenter of an earthquake by reading and interpreting seismograms How P and S waves are useful to determine where an earthquake happened Types of faults and how the hanging wall moves in relation to the fault plane Rock stress associated with fault types Review all notes and activities Review all old quizzes