Mountain Building and Faults

Name:______________________________________ Block:________
Mountain Building and Faults
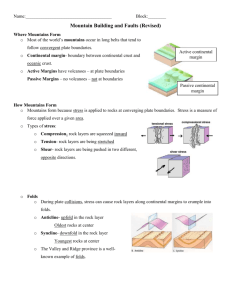
Where Mountains Form o Most of the world’s mountains occur in long belts that tend to follow convergent plate boundaries. o Continental margin- boundary between continental crust and oceanic
Active continental margin crust.
Passive continental margin
How Mountains Form o Mountains form because stress is applied to rocks at converging plate boundaries. o Types of stress: o Compression - rock layers are squeezed inward o Tension - rock layers are being stretched o Shear - rock layers are being pushed in two different, opposite directions. o Folds o During plate collisions, stress can cause rock layers along continental margins to crumple into folds. o Anticline - upfold in the rock layer o Syncline - downfold in the rock layer o The Valley and Ridge province is a well known example of folds.
o Faults o A fault is a break in the lithosphere along which movement has occurred. o Normal fault - hanging wall moves down with respect to the footwall o Reverse fault - with the hanging wall move up with respect to the footwall o Thrust fault - reverse fault in which the fault plane dips 45
or less from the horizontal. o Strike-slip fault - rocks on opposite sides of the fault plane move horizontally. The San Andreas is a well known strike-slip fault. o Horsts and Grabens - occurs from tensional stress and normal faulting.
Types of Mountains o Folded Mountains -Two plates carrying continental crust collide.
Ex: Appalachians and Himalayas o Dome Mountains - individual, isolated structures that occur in flat lying rock. A nearly circular folded mountain. o Volcanic Mountains - Occurs when there is a collision between an oceanic plate and continental plate and subduction occurs. The volcanic mountains form on the continental plate. o Fault-Block Mountains - In areas where the crust is uplifted it forms normal faults. The tension and uplift causes whole blocks of crust to be pushed up.
Folded Mountains