Chapter 14 Reading Assignment #1
advertisement

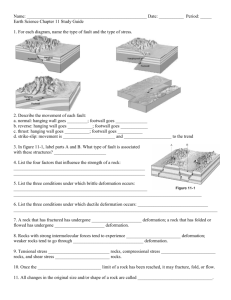
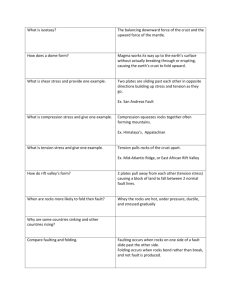
Chapter 11 Guided Reading Assignment #1 1. Read: 307-313 2. Define the following terms: a) b) c) d) e) Deformation Stress Strain Anticline Syncline f) g) h) i) j) Monocline Normal Fault Reverse Fault Thrust Fault Strike-slip Fault 3. List the four key concept questions for this section. 4. How do continents grow? 5. Every rock has a point at which it will ____________. 6. When do rocks begin to deform? 7. In the table below, summarize the 3 factors that influence the strength of a rock and how it will defore. Factor Summarization 1. Temperature and 2. Pressure 3. 1. Rock Type 2. 3. 1. Time 2. 3. 8. Why are sedimentary rocks more likely to deform? 9. What is meant by ductile deformation? 10. What is meant by brittle deformation? CPHS Physical Geology Mr. G. Edelman 11. List the three types of stresses that rocks commonly undergo. 12. ____________ is caused by rocks being pulled in opposite directions. 13. List the three types of folds. 14. How are anticlines and synclines different? 15. ________occur as sedimentary layers have been folded over a large faulted block. 16. List the 3 major types of faults. 17. Where are the hanging wall and footwall found? 18. The movement in normal faults is mainly in a ____________________. 19. How are normal and reverse faults different? 20. Explain how older rocks end up on top of younger rocks. 21. Explain how thrust and reverse fault different. 22. __________________ consist of a zone of parallel fractures. 23. How are joints different from faults? 24. In the table below, answer the 4 key concept questions for this section What determines the strength of a rock? What are the types of stresses that affect rocks? What are the three main types of folds? What are the main types of faults? 25. Do 1-8 on page 313 “ CPHS Physical Geology Mr. G. Edelman