CHEMISTRY 161 - Seattle Central College
advertisement

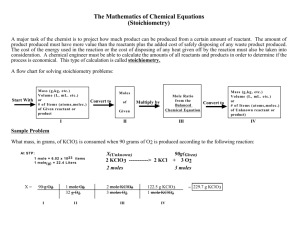
CHEMISTRY 161 PREMIDTERM #2 1. A mixture of KCl and KClO3 weighing 1.80 grams was heated; the dry O2 generated occupied 1.40 X 102 mL at STP. What percent of the original mixture was KClO3, which decomposes as follows: 2KClO3(s) 2KCl(s) + 3O2(g) 2. At what conditions (temperature and pressure) is a sample of water vapor (H 2O g) likely to become a real gas? 3. Real gasses have pressures that are lower when compared to a corresponding ideal gas. What non ideal gas factor causes real gasses to have lower pressures? 4. In Bohr’s atomic theory what is required to move an electron from an energy level closer to the nucleus to an energy level farther away from the nucleus? 5. A sample of solid potassium chlorate KClO3 was heated in a test tube and the oxygen produced was collected by water displacement at 22°C at a total pressure of 754 torr. The volume of the gas collected was 0.650 L, and the vapor pressure of water at 22°C is 21 torr. Calculate the partial pressure of oxygen in the gas collected and the mass of KClO3 in the sample that was decomposed. KCLO3 MnO2 2 KCl + 3 O2 6. Describe at least one reasonable criticism of Bohr’s atomic model. 7. How many electrons can be described by the quantum numbers n = 3, l = 3, ml = 1? 8. How many electrons fill the following a. A d orbital? b. The fifth energy level? c. A p sublevel? 9. Consider the following combinations of quantum numbers. Describe which ones are not permissible solutions of the Schrödinger equation for the electron in the hydrogen atom (i.e., which combination of quantum numbers is not allowed)? Explain why! a) b) c) d) n 9 8 6 6 l 8 2 –5 5 m –4 2 –1 –5 s (or ms) 1/2 1/2 1/2 ½ 10. List 5 ions that are isoelectronic with Ne 11. Explain why work is not a state function and altitude is a state function. 12. What is measured by constant volume calorimetry? 13. A 5.00 g sample of aluminum pellets (specific heat capacity = 0.89 j/g-°C) and 10.0 g of iron pellets (specific heat capacity = 0.45J/g-°C) are heated to 100.0°C in boiling water. The mixture of hot iron and aluminum is then dropped into 97.3 g of water at 22.0°C. Calculate the final temperature of the metal and water mixture, assuming no heat loss to the surroundings. 14. The standard enthalpy of formation of H2O (l) at 298 K is -285.8 kJ/mole. Calculate the change in internal energy for the following process at 298 K and 1 atm pressure. H2O (l) H2(g) + ½ O2(g) E = ? 15. The work function is defined as the minimum amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom by electromagnetic energy. What happens to the energy in excess of the work function from electromagnetic energy that strikes an electron? 16. State two physics experiments that suggest that electrons have quantized energy states? 17. Calculate the electron affinity of Mg2+ if its first ionization energy is 735 kJ/mole and its second ionization energy is 1445 kJ/mole. 18. Calculate the wave length of an electron traveling at 3.00 X 10-7 m/s