Molar mass
advertisement

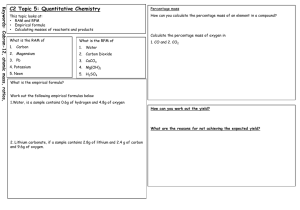
1 Chapter 3 Stoichiometry: Ratios of Combination 2 3 Mass % = [(mass of component)/(total mass)] x 100 4 5 6 111.70 100 = 69.9% Fe 159.70 What is the % oxygen in this sample? (hint :100%) % by mass = 7 8 9 10 11 • Equations can represent physical changes: KClO3(s) KClO3(l) or chemical changes • Note the symbol for heat above the arrow: 2 KClO3(s) 2 KCl(s) + 3 O2(g) 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Exercises: 19 20 (Molecular mass)/(Empirical mass) = n and Molecular formula = (Empirical formula)n 21 22 23 • The data given allows an empirical formula determination with just a few more steps. • The mass of products (carbon dioxide and water) will be known so we work our way back. 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Eercise Zn(s) + 2 HCl(aq) ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) Theoretical yield = 2.14 g ZnCl2 Actual yield ZnCl2 = 1.58 g The % yield is: 1.58g % yield = 100 73.8% 2.14g 41 Reaction Types • Combination: one product is formed • Decomposition: one reactant produces more than one product • Combustion: a hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water 42 43 44