Carbon Compounds .
advertisement

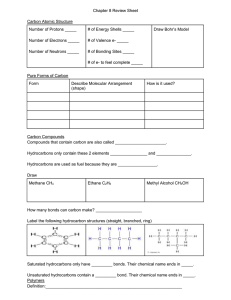
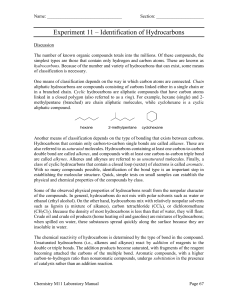
Carbon Compounds . Saturated Hydrocarbons • A Hydrocarbon is an organic compound that contains only the elements hydrogen and carbon. • In a saturated hydrocarbon, all the bonds are single bonds. • Alkane is another name for a saturated hydrocarbon. Ethane Characteristics of Hydrocarbons • Factors that determine the properties of a hydrocarbon are: • The number of carbon atoms • How the atoms are arranged: Straight chain Branched chain Ring Straight Chains • A hydrocarbon can contain one carbon atom, as in methane or thousands of carbon atoms, as in cellulose One carbon Two carbon Three carbon Four carbon Five carbons Six carbon Methane ethane propane butane pentane hexane Halosomers Branched Chains • The structural formula for certain alkanes can differ. • Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas are isomers. The Ring • Carbons can be arranged in a ring, such as cyclobutane. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons • A hydrocarbon that contains one or more double or triple bonds is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. • There are three types of unsaturated hydrocarbons alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic hydrocarbons. Alkenes • Many fruit bearing plants produce ethene, which controls the rate at which fruits ripening. Alkynes • Alkynes are the most reactive hydrocarbon compounds. • They produce extremely high temperatures while burning. Aromatic Hydrocarbons • These alternating single and double bond hydrocarbons form a ring. • Many of these compounds have strong aromas or odors. Fossil Fuels • Three types of fossil fuels are coal, petroleum, and natural gas. • The primary products of the complete combustion of fossil fuels are carbon dioxide and water Substituted Hydrocarbons • The functional group in an alcohol is a hydroxyl group, -OH. • The functional group in an organic acid is a carboxyl group,COOH. • The functional group in an amine is an amino group, -NH2 Alcohols • When a halocarbon reacts with a hydroxyl group. Polymers • Polymers can be classified as natural polymers or synthetic polymers. • Rubber, nylon, and polyethylene are three examples of compounds than can be synthesized. Types • Four types of polymers produced in plant and animal cells are: • Starches • Cellulose • Nucleic acids • Proteins