ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Chapter 22.1 Hydrocarbons
advertisement

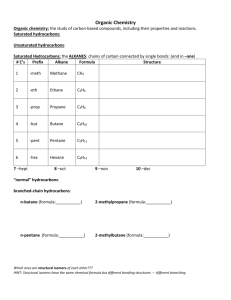
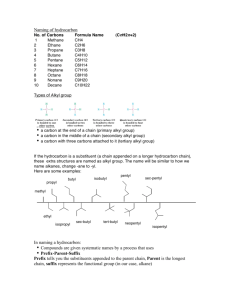
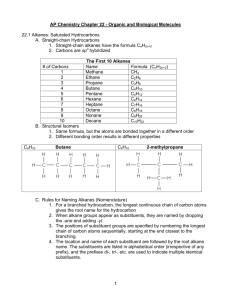
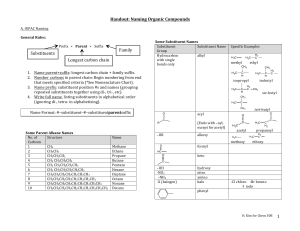
Naming, Drawing, and Properties They are all around us! Gasoline, Fuels, and Kerosene are all example of hydrocarbons. What two elements make up a hydrocarbon? The simplest organic compounds contain only carbon and hydrogen and are called hydrocarbons. Carbon has four valence electrons… Therefore, it can form a max of 4 single covalent bonds with hydrogen: Get a glimpse of the staggering variety of hydrocarbon compounds. file:///D:/Chapter22/Section01/ChemASAP/d swmedia/rsc/asap1_chem05_cman2228.html Formulas and Models for Methane and Ethane Ball-and-stick model Space-filling model An alkane is a hydrocarbon in which there are only single covalent bonds. The carbon atoms in an alkane can be arranged in a straight chain or in a chain that has branches. Next lesson, we will look at Alkenes and Alkynes too. Ethane is the simplest of the straight-chain alkanes, which contain any number of carbon atoms, one after the other, in a chain. Above are the first 10 straight chained alkenes. Draw the structural formulas for methane through pentane. Get a ball and stick model kit. Construct a ball and stick model of methane. Show teacher. Construct a ball and stick model of butane. Question: How many covalent bonds are there in butane? An atom or group of atoms that can take the place of a hydrogen atom on a parent hydrocarbon molecule is called a substituent. A hydrocarbon substituent is called an alkyl group. An alkane with one or more alkyl groups is called a branched-chain alkane. Redraw with hydrogens… 1. Find the longest chain of carbons: Whether it is in a straight line or not. This will be the parent name 2. Number the carbons in the parent chain. Number them in a way where the substituents have the lowest numbers possible. 3. Add the number as a prefix to the substituents name to identify the position. 4. Use word prefixes (di, tri, tetra, etc.) if a substituent is used more than once. 5. List the names of substituents in alphabetical order. Ignore prefix names when alphabetizing. 6. Use a comma to separate numbers. Use hyphens to separate numbers and words. Full name should contain no spaces. Distinguishing Parent Structure from Substituents Steps: 1. Find the root word ending in –ane in the hydrocarbon name. Then write the longest carbon chain to create the parent structure. 2. Number the carbons on the parent chain. 3. Identify the substituent groups. Attach to the appropriate number on parent chain. 4. Add hydrogen as needed. 4-ethyl-2,3,4-methyloctane LIKE DISSOLVES LIKE In terms of: Polar and Non-Polar molecules Hydrocarbons are non-polar: Can be dissolved by other non-polar compounds. Will hydrocarbons dissolve in water? Why or why not? Section Assessment 22.1 on page 701