here - CeNSE - Indian Institute of Science
advertisement

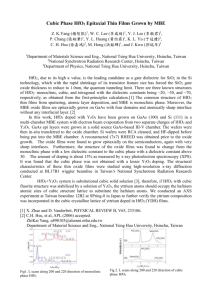
New Substrate for High Performance Graphene transistors Kolla Lakshmi Ganapathi, Navakanta Bhat and Sangeneni Mohan Centre for NanoScience and Engineering (CeNSE), Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore-560012, India SiO2(300 nm)/Si substrate has been extensively used for back-gated graphene transistors, because graphene can be easily visualized using optical microscope on a 300nm SiO2 layer on Silicon, due to optical interference. But this substrate can limit the device performance due to low gate coupling, resulting from low dielectric constant and high thickness of SiO2 gate dielectric. This in turn requires high gating (switching) voltages. We optimized HfO2 films for high performance back-gated graphene transistor, using electron beam evaporation. Bilayer graphene is exfoliated on HfO2(32nm)/Si substrate, and identified using optical microscopy and subsequently confirmed with Raman spectroscopy. High performance HfO2 back-gated graphene transistor has been fabricated. We demonstrate highest transconductance reported till date (60 S at Vds=100mV), for back-gated bilayer graphene transistor. The transconducatance is about 20 times higher than SiO2(300 nm)/Si substrate. The optimized HfO2 films also result in slightly lower tarp density compared to SiO2. For details: Kolla Lakshmi Ganapathi, Navakanta Bhat, and Sangeneni Mohan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 073105 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4818467 Fig. (a) Bilayer graphene transistor on 32 nm HfO2/Si substrate (b) C-V characteristics on HfO2 indicating high-k value (18.9) (c) Ids–Vg /Vgmax curves at Vds = 10 mV, (inset HfO2/Si, Vds = 100 mV). (d) gm–Vg /Vgmax curves at Vds = 10 mV, (inset HfO2/Si, Vds = 100 mV). (Note: Vgmax=80V for SiO2 and Vgmax=4V for HfO2)