03. - Editorial Digital Tecnológico de Monterrey
advertisement

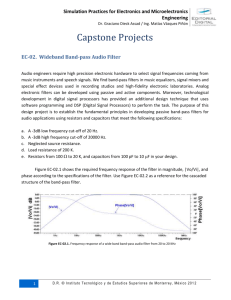
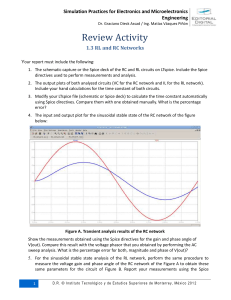
Simulation Practices for Electronics and Microelectronics Engineering Dr. Graciano Dieck Assad / Ing. Matías Vázquez Piñón Capstone Projects EC-03. Low Pass and High Pass Noise Filters Instrumentation and biomedical engineers require reliable electronic circuits to reject noisy signals coming from working environments, HVAC systems and other electronic equipment. Data acquisition systems, signal converters and common mode noise filtering devices in power plants, factories, hospitals, commercial buildings, houses and laboratories use low pass and high pass filters. Electronic noise filters can be designed using both, passive and active components. Also DSP (Digital Signal Processors) can be used with software programs to perform the task. With this design project we seek to establish the fundamental principles in developing passive low pass and high pass noise filters for a wide variety of applications using resistors and capacitors. The objective of this capstone project is to design and simulate a low pass noise filter that rejects noise signals higher than 5 KHz, and to design and simulate a high pass filter that rejects noise below 50KH. These are the specifications: a. b. c. d. e. For the low pass filter: a -3dB low frequency cut-off of 5000 Hz. For the high pass filter: a -3dB high frequency cut-off of 50000 Hz. Neglected source resistances. Load resistances of 100 K. Resistors from 100 to 20 K, and capacitors from 100 pF to 10 F in your design. Figure EC-03.1 shows the required frequency response of the low pass filter in magnitude, |Vo/Vi|, and phase according to the specifications of the filter. Figure EC-03.2 illustrates the required frequency response of the high pass filter in magnitude an phase. 1 D . R . © I n s t i tu t o T e c no l ó g ic o y d e E s t u d i o s S u p er i o re s d e M o n te rr e y , M é x i c o 2 0 1 2 Simulation Practices for Electronics and Microelectronics Engineering Dr. Graciano Dieck Assad / Ing. Matías Vázquez Piñón Figure EC-03.1. Low pass filter frequency response Figure EC-03.2. Required frequency response of the high pass filter in magnitude an phase 2 D . R . © I n s t i tu t o T e c no l ó g ic o y d e E s t u d i o s S u p er i o re s d e M o n te rr e y , M é x i c o 2 0 1 2 Simulation Practices for Electronics and Microelectronics Engineering Dr. Graciano Dieck Assad / Ing. Matías Vázquez Piñón Report. 1. Provide the circuit schematic and analytical solution for both, low pass and high pass designs. 2. Describe the loading effects that the circuit may have while selecting the resistor values. 3. Include the frequency domain simulation of the circuit using an AC analysis in magnitude and phase of the transfer characteristic of each filter. 4. Include the measurement of the -3dB frequency cut-offs for both filters. Here, you must measure magnitude and phase of the transfer characteristic. 5. Include measurement of magnitude and phase of the response at the low frequency, about 1 KHz for the low pass, and at high frequency, about 1 M for the high pass. 6. Compare the simulated response to the analytical solution in magnitude and phase for both frequency responses. 7. What parameters are desirable to change if we want to change the specified cut-off frequencies? 8. Discus the possible sources of errors, loading effects and personal observations when performing the analysis and the simulation experiment. 9. Include references. 3 D . R . © I n s t i tu t o T e c no l ó g ic o y d e E s t u d i o s S u p er i o re s d e M o n te rr e y , M é x i c o 2 0 1 2