UV-Vis and Fluorescence
advertisement

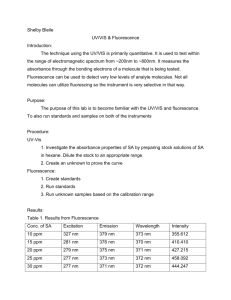
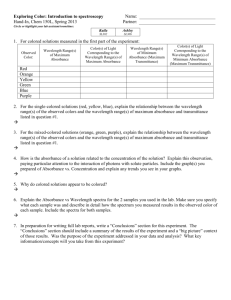
Tim Abell UV-Vis and Fluorescence Introduction UV-Vis is a spectrophotometer that operates in the ultraviolet and visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum. It is used to analyze compounds through absorbance of radiation. It can be used to determine the maximum absorbance of a compound. Fluorescence detects the emission of radiation after if excites the electrons of the compound. It can detect very low concentrations of analytes. It can be used to determine the concentrations of analytes. Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to explore the absorbance properties of salicylic acid (SA) in hexanes with the UV-Vis. Then determine the concentration of SA in old aspirin. The concentration of quinine in tonic water will be determined with fluorescence. Method (UV-Vis) 1. 2. 3. 4. Turn on instrument (switch located at the rear left) Turn on computer and double click on Vision Pro Software on the Desktop Allow the instrument to initialize for 10-15 minutes In the toolbar frame, select the scan icon a. In the menu, enter: wavelength 190-400nm, absorbance, and Tungsten lamp 5. Click Baseline Correction and select 100% T 6. Click on the Baseline Zero icon (looks like a graph with two arrows pointing down) 7. Insert quartz cuvette with hexane a. Wash the cuvette 3 times, fill ¾ full, then wipe with Kimwipe 8. Click run icon 9. To see peaks, click on the graph window, then Graph in the menu. Select peak labels. Select wavelength and value. 10. Click graph in the menu and select track, then click the graph window 11. Use the keypad to find the peak and record wavelengths and absorbance 12. Repeat from step 7 using standard solutions Data (UV-Vis) Concentration (ppm) Absorbance 10 20 30 40 50 0.154 0.386 0.372 0.816 1.038 UV/Vis Calibration 1.2 y = 0.022x - 0.1062 R² = 0.9216 Absorbance 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Concetration (ppm) Sample Mass (g) Aspirin 0.0045 Volume hexane (mL) 100 Absorbance 0.212 SA Concentration (ppm) 14.46 Method (Fluorescence) 1. Turn on instrument (switch located at the front right) 2. Turn on computer and open the PX-150x Program 3. Make sure the instrument is on: a. In the menu, go to configure, select PC Configuration, and select port 1 b. In the menu, go to configure, select instrument, and select On 4. Set the instrument to quantitative analysis by going to Acquire mode in the menu, and selecting Spectrum. 5. Obtain stock solution and dilute a. Wash a quartz cuvette 3 times with the smallest concentrated solution, and set the following parameters: b. Select Configure in the menu, and select Parameters i. Spectrum Type: excitation ii. EM Wavelength: 400nm iii. EX Wavelength Range: 200-900nm iv. Sensitivity: Low v. Scan Speed: Fast vi. Recording Range: -10.00 to 500 vii. EX/EM slit width: 10/10 viii. Response Time: 0.02 6. Click run 7. After this first run, click search (lambda). Set the ranges to the following: a. EX: 230-450nm b. EM: 240-650nm 8. Click Search and note the optimal wavelengths for EX and EM. 9. Change the parameters by selecting Configure in the menu, and select Parameters a. Change the spectrum type to emission b. Change the excitation wavelength to the optimal wavelength found c. Be sure the emission wavelength range encompasses the optimal EM wavelength found 10. Run other samples and record the wavelength and intensities of the largest peak To view peaks, click Manipulate in the menu and select peak pick. Expand the window to note peaks. Data (Fluorescence) Excitation: 371 nm Concentration (ppm) 0.1 1 5 10 Emission: 448 nm Intensity Wavelength (nm) 29.354 448 183.714 450 1014.471 447 1014.49 493 Fluorescence Calibration y = 104.23x + 140.98 R² = 0.7952 1400 1200 Intensity 1000 800 600 400 200 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Concentration (ppm) Sample Tonic Water Intensity 1014.490 Wavelength (nm) 499 Concentration (ppm) 8.38 Calculations Sample preparation Stock solution= 1000 ppm M1V1=M2V2 (1000 ppm)V1=(10 ppm)(10 mL) V1= 0.1 mL Salicylic Acid Concentration 0.212=0.022x - .1062 x= 14.46 ppm Quinine in Tonic Water Concentration 1014.49=104.23x + 140.98 x= 8.38 ppm Conclusion The experiment with the UV-Vis was successful. We created a calibration curve with standards of SA in hexanes. The R squared value (0.9216) was decent but could have been improved if we had more time. Since the calibration curve was not great the calculated concentration of SA in the aspirin sample is not very accurate. The experiment with fluorescence was not as successful. We had problems with the lack of detail in the SOP. Our R squared value (0.7952) was not good at all. We did not have enough to create a new calibration curve. Due to our poor calibration curve the concentration of quinine in the tonic water is not accurate.