Important topics to review for the final exam
advertisement

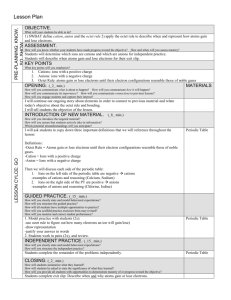
A list of topics and subtopics to study for CHEM 231 final exam The most important topics; those which are emphasized or are vital for subsequent understanding are marked *. Exam 1 Topics Compounds, elements, mixtures (heterogeneous & homogeneous) Names and symbols of elements* Unit conversions; compound units* Density problems Atomic structure* Electrons, protons, neutrons Isotopes Average atomic weights Classic experiments: Rutherford, Millikan, etc. Periodic table* Names of groups Other divisions: metals, main groups, transition elements Ions: names and charges Monatomic ions from periodic table Polyatomic ions Names and formulas* Ionic compounds Simple common covalent compounds and diatomic elements Acids Simple organic compounds (including structures) Exam 2 Topics Chemical equations* Reactant, product, phase notation Balancing Empirical formulas; mass percents of elements Formula weights* Avogadro number and molar quantities Stoichiometry* Relating reaction masses Limiting reactants Solutions; solvents and solutes Electrolytes: ions in aqueous solution* Reaction types* Oxidation-reduction; acid-base Decomposition; combination Solution reactions* Double displacement type: Precipitation and acid-base (hydroxides, carbonates)* Single displacement: Oxidation of metals by metal ions or acids* Net ionic equations; spectator ions Other reactions: Combustion, e.g. Solution concentrations* Units: Percent, molarity Making solutions & diluting Solution stoichiometry Titrations Exam 3 Topics 1st law of Thermodynamics Work, heat, energy, enthalpy Energy units: J, cal, eV, kJ/mole Heat & temperature* Heat capacity, specific heat & molar heat capacity Reaction enthalpies* Hess’s Law Heat of formation & combustion Using tabulated thermodynamic data Thermochemical equations & stoichiometry Energy conversions Bond energies Electromagnetic spectrum* Wavelength, frequency, photon energy Regions of spectrum & processes Matter waves; uncertainty principle Energy levels and wave functions for atoms and molecules* Photon absorption and emission; calculate wavelengths Electron states of hydrogen: shells, subshells, orbitals & quantum numbers Electron structure of many-electron atoms* Electron spin and Pauli principle Electron configurations; relation to periodic table Exam 4 Topics Energies of electrons in atoms Inner shell & valence electrons Effective nuclear charge; shielding Periodic trends of atomic properties Size of atoms Ionization energy & electron affinity Electronegativity Metallic nature of elements Lattice energies & Born-Haber cycles Lewis electron dot structures* Atoms and atomic ions Simple molecules; counting valence electrons Octet rule Formal charges & oxidation numbers Violations of octet rule Resonance structures Reactions Oxidation of metals (by acid, water, other metal ions, halogens) Metal oxides as bases Nonmetal oxides as acids Activities of metals Unit 5 Topics Predicting geometry from Lewis structures* Electron domains Molecular geometries Bond angles Dipole moments Hybridization Double and triple bonds Sigma and pi bonds Delocalized pi orbitals Gas laws* Boyle’s, Charles’ , Avogadro’s Laws Ideal gas law Stoichiometry involving gases* Kinetic theory of gases Assumptions of the model Explanations of gas behavior Emphasized throughout Estimating numerical answers* Language of chemistry: translating words into chemical equations* Unit analysis*