AP Chemistry- Midterm Review by Topic Chapter One: Introduction
advertisement

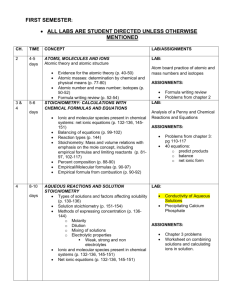
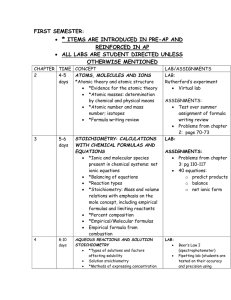
AP Chemistry- Midterm Review by Topic Chapter One: Introduction: Matter and Measurement Definition of chemistry Chemistry applications Definitions of matter, Characteristics of mixtures Definition of physical & chemical change Scientific Notation* Significant figures* Math functions using significant figures Density calculations* Unit Conversions using dimensional analysis* Divisions of chemistry Scientific method States of matter, Classification of matter Qualitative vs. quantitative Accuracy and precision Metric prefixes* SI units of measure* Qualitative vs. Quantitative Conversion Kelvin/Celsius* Chapter Two: Atoms, Molecules and Ions Define atom Properties of protons, neutrons, electrons Atomic Mass Isotopes Define groups/families on the periodic table Define chemical formula, formula unit Write balanced formula unit (ionic) Calculate empirical and molecular formulas* Atomic structure Atomic number Calculate average atomic mass* Organization of the Periodic table Family properties Recognizes ions and charges Write molecular formulas (covalent) Identify common acids Chapter Three: Chemical Reactions Write/balance equations Solution process & solubility Neutralization reaction and net ionic Redox Reaction and net ionic equations Predict products based on the type of reaction Identify strong electrolytes Write net ionic equations Oxidation Numbers* Apply solubility rules & activity series ½ reactions for redox Chapter Four: Stoichiometry Chemical Analysis Apply mass relationship to chemical equations* Theoretical and % yield Preparation of Solutions & dilutions Aqueous Stoichiometry Empirical formula based on combustion Limiting reactants Solution Concentration (Molarity) Beer’s Lambert Law Titration Chapter Five: Thermochemistry Define energy and units in measuring energy Enthalpy of reactions (ΔH) and associated calculations* Understand heat flow (endo/exo) Hess’s law and applications Specific Heat Calorimetry Enthalpy of formation (ΔHf) Chapters Six: Structure of Atoms Chapter Seven: Periodic Trends Wave nature of light Electromagnetic radiation Relationship of wavelength, frequency and speed of light Line spectra Energy and electron transition Quantum numbers Periodic trends: ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic radius) Role of electron shielding and affective nuclear charge Isoelectronic series Assign electron configuration, Orbital filling rules Chapter Eight: Chemical Bonding Chapter Nine: Bonding and Molecular Structure, Orbital Hybridization Electronegativity Valence electrons & dot notation Lewis structures and multiple bonds Formal charge Hybridization types of chemical bonds Lewis structures for compounds Lewis structures and resonance Exceptions to the Octet Rule Sigma, pi bonds VSEPR Molecular Shape Molecular polarity Bond Order, bond length Electron domain Lone pair, bonded pair electrons Bond dipole Bond enthalpy & enthalpy of reaction Chapter Eleven: Gases and their Properties Combined gas law Gas density/molar mass Dalton’s law of partial pressure KMT – conceptual Ideal gas law Avogadro’s law Gas stoichiometry Effusion/Diffusion Chapter Twelve: Intermolecular Forces and Liquids Chapter Thirteen: Chemistry of Solids Intermolecular force of attraction (IMF) Born-Haber Cycle (lattice energy) Vapor Pressure Properties of water surface tension Energy Diagram and phase change Phase Diagram Chapter Fourteen: Solutions and Their Behavior Solution Process Concentration (M, m, % mass, mole fraction)* Solubility Vapor pressures of solutions Boiling point elevation* Osmotic pressure* Types of Solutions Energy of solution formation Solubility Curve Raoult’s law Freezing point depression* Van’t Hoff Factor *Be able to solve problems by performing calculations (similar to previous tests and worksheets).