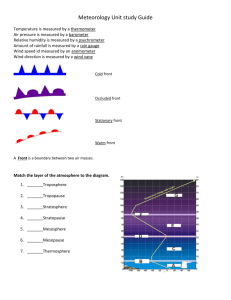
latitudes forecasting
Name________________________________ Block: __________
Forecasting Notes Part 1
Climate o An area’s long- term pattern of weather (30 years) o Controlled by latitude, elevation, nearby water, ocean currents, topography, prevailing winds and vegetation
Weather o It’s what’s happening outside now! o It’s a result of humidity
Air pressure
Condensation
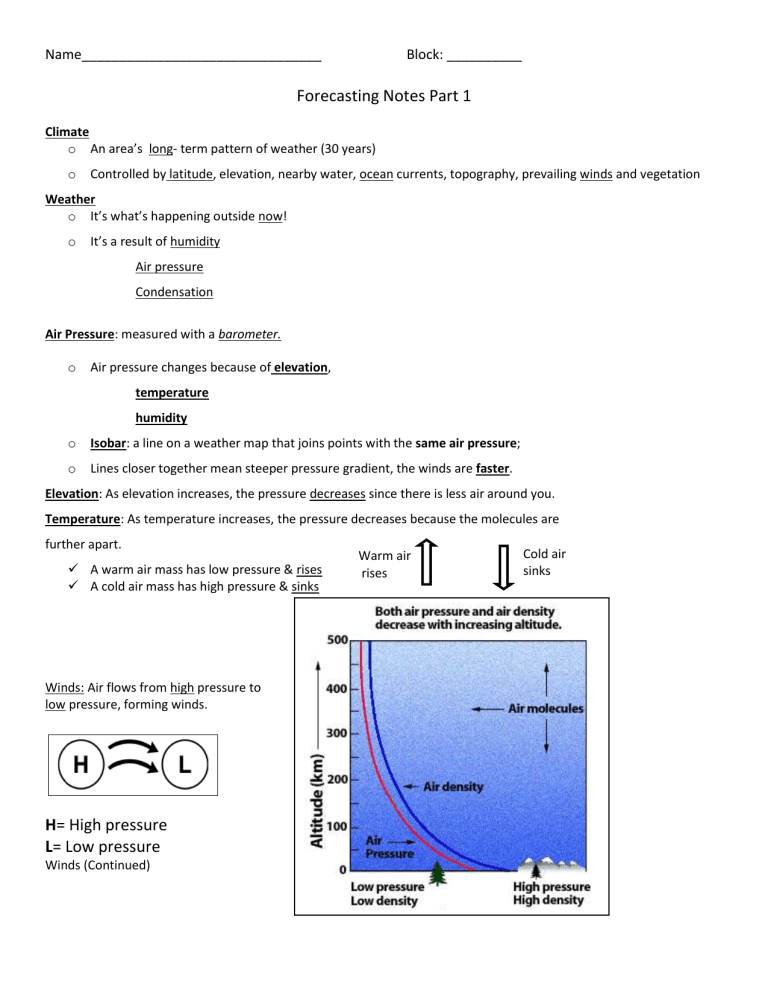
Air Pressure: measured with a barometer. o Air pressure changes because of elevation, temperature humidity o Isobar: a line on a weather map that joins points with the same air pressure; o Lines closer together mean steeper pressure gradient, the winds are faster.
Elevation: As elevation increases, the pressure decreases since there is less air around you.
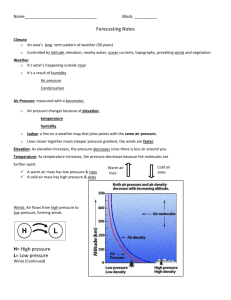
Temperature: As temperature increases, the pressure decreases because the molecules are further apart.
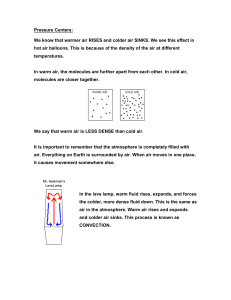
A warm air mass has low pressure & rises
A cold air mass has high pressure & sinks
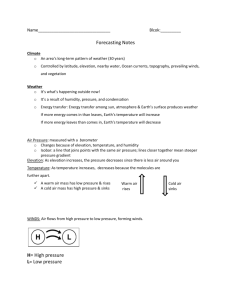
Winds: Air flows from high pressure to low pressure, forming winds.
H= High pressure
L= Low pressure
Winds (Continued)
Warm air
rises
Cold air sinks
o Air over land cools faster & heats faster than air over water. o Sea breeze: when winds blow inland from the ocean, because a warm low pressure area is over the land o Land breeze: when winds blow off the land to the ocean because a warm low pressure area is over the ocean o Anemometer measures wind speed.
Factors effecting winds: Coriolis Effect
Hurricanes in the Northern Hemisphere rotate counterclockwise while hurricanes in the Southern Hemisphere rotate clockwise.
Coriolis effect: the tendency of an object moving freely over Earth’s surface to curve away from its path of travel, caused
by the Earth’s rotation.
Jet Stream: a band of swiftly moving wind, moving East from the West, at the top of the troposphere, unaffected by friction
Global Wind Patterns: o Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), also known as the doldrums : low-pressure zone near equator caused by warm, rising air o Trade winds: 5-20° latitudes - warm & steady winds o Subtropical highs: 20-35° latitudes - air usually sinks - very dry w/ little wind - deserts o Polar highs: high pressure regions near the poles (sinking air) - very dry