Meteorology Unit study Guide Temperature is measured by a
advertisement

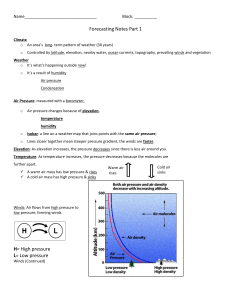
Meteorology Unit study Guide Temperature is measured by a thermometer Air pressure is measured by a barometer Relative humidity is measured by a psychrometer Amount of rainfall is measured by a rain gauge Wind speed id measured by an anemometer Wind direction is measured by a wind vane Cold front Occluded front Stationary front Warm front A Front is a boundary between two air masses. Match the layer of the atmosphere to the diagram. 1. _______Troposphere 2. _______Tropopause 3. _______Stratosphere 4. _______Stratopause 5. _______Mesosphere 6. _______Mesopause 7. _______Thermosphere We live in the troposphere. Climate is an area’s long term pattern of weather. The coriolis effect is responsible for hurricanes rotating counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and for them rotating clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. Coriolis effect is the tendency of an object moving freely over Earth’s surface to curve away from its path of travel, caused by the Earth’s rotation. Cloudy nights can be warmer than clear nights because clouds trap heat absorbed by Earth during daylight hours Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC’s) contributes to the deterioration of the ozone layer Pressure differences are responsible for creating the sea breeze and the land breeze. Sunshine occurs with a high pressure system. Ocean currents, topography and latitude help determine the climate of an area. Gases in the atmosphere absorb and trap heat: this is called the greenhouse effect. Air moves from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. (HL) Millibars is the unit for air pressure. The air temperature and dew point are the same when the humidity is 100%. The H on a weather map is high pressure and the L is low pressure. Lines of equal pressure on a weather map are isobars. The wind blows faster when the isobars are closer together. Lines of equal temperature on a weather map are isotherms. Winds curve to the right in the Northern Hemisphere. The doldrums: a low-pressure zone near equator caused by warm, rising air, with very little wind. Jet Stream: a band of swiftly moving wind, moving East from the West, at the top of the troposphere, unaffected by friction Hurricanes need warm ocean water to form. “Tornado Alley” is a location in the United States where numerous tornados form each year. Sleet are raindrops that have frozen as they fall through cold air. Freezing rain is when the raindrops freeze when they come into contact with a solid surface. Sea breeze: when winds blow inland from the ocean, because a warm low pressure area is over the land Land breeze: when winds blow off the land to the ocean because a warm low pressure area is over the ocean. There are 4 types of air masses: 1. Continental polar (cP): cold and dry 2. Continental tropical (cT): warm and dry 3. Maritime polar (mP): cold and wet 4. Maritime tropical (mT): warm and wet


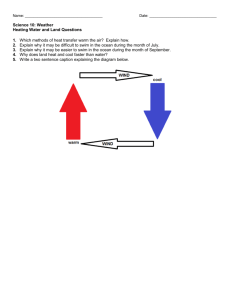
![wind [Repaired]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009822995_1-d740f770c04b871f35a8b5ad3684a975-300x300.png)