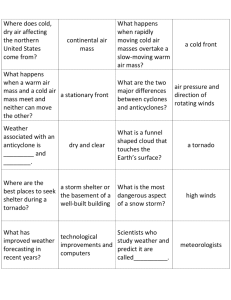
Weather Unit Part One: Warm fronts and cold fronts are caused by
advertisement

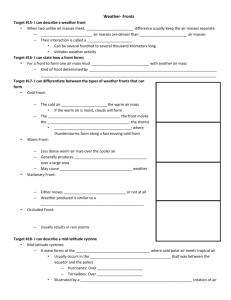
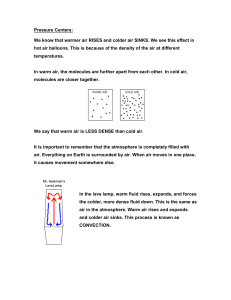
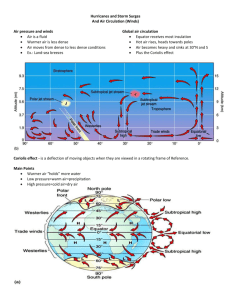
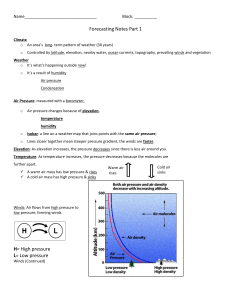
Weather Unit Part One: Warm fronts and cold fronts are caused by _______________________. Before During After Cold Front Warm Front Stationary Front Occluded Front Remember: _______________sinks, ________________ rises Cold Front: Form where _____________________ moves towards ___________________ o This creates __________________________ Draw the cold front symbol Warm Front: form where ________________ moves towards ______________________. Draw the warm front symbol Occluded Front: When a __________________________ overtakes a ____________________ and forces it up (___________) Draw the Occlued Front symbol Stationary Front: When a ________________________ and ___________________________ can not over take each other (________) Draw a Stationary Front: Match: A: B: C: D: Air pressure… Driven by the _________ ______________ matter and energy Challenge Activity: Warm Front? _____ Cold Front? ______ Occluded Front?______ Stationary Front? _______ High Pressure? _______ Low Pressure? _______ Cyclone? ______ _______ Rises (_________) Wind _____________________ __________ Sinks (___________) Part II: _______________________: A rotating tropical storm with severe winds Wind must be _______ miles (______ kilometers) per hour or greater. Accompanied by _________, ____________________, and ___________________. Usually originate near the equator and travel ______________ or ___________________ in the Northern Hemisphere (______________________ _________________) The _____________ has a ___________ pressure system Hurricanes love ___________ water and ___________ strength Category One Wind Storm Surge Damage Two Three Four Five How does a storm surge increase coastal flooding? ____________________: A mobile, destructive ____________ of violently rotating wind having the appearance of a __________________-shaped cloud and advancing beneath a large storm system. o Categories ______ to ________ (__________ destructive) o __________ pressure system in middle o A tornado over water is called a _________________________. o Tornado safety: Stay Go to the Last resort o Most tornadoes occur in _______________ ______________________: A severe snowstorm with high winds and low visibility. o Most important rule: _______________________________________ o Rule #8: _____________________: A storm in which snow or rain freezes on contact, forming a coat of ice on the surfaces it touches o Be proactive: o Why do you not run a generator inside? ______________________: A storm with thunder and lightning as well as heavy rain or _______________ o What do you do if you are stuck outside during a thunderstorm? Part THREE: ____________________: A measure of the average kinetic energy (_______________) of individual molecules in matter. Atoms and molecules (_____________________) are in constant motion. o The high the temperature: o Increased heat energy makes atoms: ______________________: a measure of the heat from expanding and contracting liquids or coils o Boiling pt of water (Fahrenheit): ____________ o Freezing pt of water (Fahrenheit): ____________ Convert 95 from Fahrenheit to Celsius: o Subtract 32 o Divide by 9 o Multiply 5 Practice: 112 F to ________C **** STOP on SLIDE 37**** 230 F to _______C 152 F to ______C Part IV: ____________________: A line drawn on a weather map or chart linking all pints of equal or constant temperature. ____________________: the study of the atmosphere that focuses on weather processes and forecasting. What layer of the earth does weather happen in? ___________________________ Climate….Driven by the ____________, ___________________ life, ____________________ over __________________ from man-made and natural causes. A ____________________ _________________________ makes continuous measurements of different aspects of the weather. Weather stations use _______________________ ___________________________ so that their readings can be compared. Weather tool Thermometer Wind Vane Anemometer Barometer Rain Guage Satellites Weather balloons What does it do Picture Isobar ****Stop at slide 94**** Part Five: The earth is floating _________________. Navigators must compensate for earth’s rotation (_______________________) Pressure gradient forces cause hurricanes to spin ______________________ of the coriolis Force but the coriolis force keeps __________________________ forming hurricanes from crossing the equator and sends them _____________. A rotating body creates weather __________________________, _______________________ _________________________, and thus has a significant impact on our ________________. ______________ is the movement of _____________________________ air on a planet, caused by the different temperatures ___________, and therefor _______ pressure differences. The _________________________: any of the high speed, high altitude air ___________________ that circle the earth in a westerly direction. Flying times can be significantly shorter going from California to New York because of this: ____________________________. Part Six: ____________: The movement of _________, from ___________ pressure to __________ pressure. The wind is caused by different ______________________ around the planet. This is caused by the _________ Weather is caused by the __________________ from the _________ being __________________ throughout earth. Ways wind is good Wind is an important _____________________ ___________________. Without wind land would not get what? ___________________ Wind ______________ to prey/predators Allows animals to ___________________ ___________ and _________________ us down. Plants use wind to ________________________ Draw this globe. We will label it together!! Doldrums_-areas of _______ wind. Occurs at the ______________________, air here heats up fast causing low pressure. Horse Latitudes: Areas of _____ wind, occurs at ______________ + ________, air stops moving towards the poles and sinks. Trade Winds- _____________ winds are blown towards the ____________________ because the horse latitudes produce areas of ________ pressure. __________________ ___________________ curves the wind!!** Prevailing Westerlies- Winds blowing towards the __________, Move from _____________ to _________________ occurs between ____________________________. Polar Easterlies-_______________air sinks and heads towards the __________________, ________________________ Effect curves the winds** The winds circulate ____________________ and _________________