Matter, Energy, and Chemistry Guided Reading & Study
advertisement

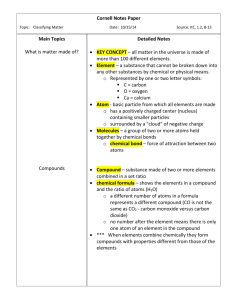
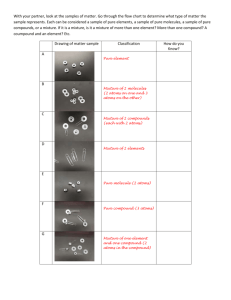
GR 2.1 Describing Matter Guided Reading and Study Use Target Reading Skills matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. chemistry is the study of the properties of matter and how matter changes. substance A substance is a single kind of matter that is pure and has a specific set of properties. physical property A physical property can be observed without changing a substance into another substance. chemical property A chemical property describes the ability of a substance to change into a different substance. element An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into any other substance by chemical or physical means. atom An atom is the basic particle of an element. chemical bond A chemical bond is a force of attraction between two atoms. molecule A molecule is a particle formed when two or more atoms are held together by chemical bonds. compound A compound is a pure substance made of two or more elements chemically combined in a set ratio. chemical formula A chemical formula shows the elements in the compound and the ratio of atoms. mixture A mixture is two or more substances that are together in the same place but are not chemically combined. heterogeneous mixture The different parts in a heterogeneous mixture can be seen. homogeneous mixture The substances in a homogeneous mixture are so evenly mixed that the different parts cannot be seen. solution A solution is an example of a homogenous mixture. 1. chemistry 2. true 3. physical 4. a. chemical b. physical c. physical d. chemical e. physical f. chemical 5. element 6. false 7. chemical bond 8. two 9. A pure substance made of two or more elements chemically combined in a set ratio 10. 1 carbon atom to 2 oxygen atoms 11. CO 12. false 13. mixture 14. a. Each substance in a mixture keeps its individual properties. b. The parts of a mixture are not combined in a set ratio. GR 2.2 Measuring Matter Guided Reading and Study Use Target Reading Skills Sample questions and answers: How are weight and mass different? (Weight is a measure of the force of gravity on an object. Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. What is volume? (Volume is the amount of space that matter occupies.) How is density determined? (Density is determined by dividing the mass of a sample of matter by its volume.) 1. weight 2. false 3. Mass is the measurement of the amount of matter in an object. 4. Unlike weight, mass does not change with location, even when the force of gravity changes. 5. the International System of Units 6. kilogram 7. volume 8. Sample answer: liter (L), milliliter (mL), cubic centimeter (cm3) 9. volume = length width height 10. Sand and feathers have different densities, and therefore, different volumes. 11. Density = [Mass/Volume] 12. Since wood floats, its density is less than the density of water, 1 g/cm3. Since iron sinks, its density is greater than the density of water. 13. false GR 2.3 Changes in Matter Guided Reading and Study Use Target Reading Skills Sample effects: One or more new substances are produced. Energy is either absorbed or released. 1. Any change that alters the form or appearance of matter but does not make any substance in the matter into a different substance 2. false 3. a, c, d 4. A chemical change is a change in matter that produces one or more new substances. 5. Unlike a physical change, a chemical change produces new substances with properties different from those of the original substances. 6. c, d 7. law of conservation of mass 8. energy 9. true 10. Temperature is the average energy of motion of the particles in matter. Thermal energy is the total energy of all the particles in an object. 11. a. exothermic b. endothermic GR 2.4 Energy and Matter Guided Reading and Study Use Target Reading Skills Sample details: a. Chemical energy is the energy stored in the chemical bonds between atoms. b. Electromagnetic energy travels through space as waves. c. Electrical energy is the energy of electrically charged particles moving from one place to another. 1. true 2. Potential, kinetic, chemical, electromagnetic, electrical, and thermal 3. kinetic 4. potential 5. b, c 6. The internal energy stored in the chemical bonds between atoms 7. b 8. Sample answer: Microwaves in a microwave oven can changes a frozen block of spaghetti and sauce into a hot meal, which is a physical change. 9. electrical 10. electrodes 11. b, d 12. false 13. electromagnetic, chemical