2-1 Describing Matter Notes Matter: anything that has mass and
advertisement

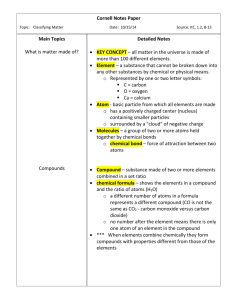
2-1 Describing Matter Notes Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space Chemistry: study of the properties of matter and how matter changes. Substance: single kind of matter that is pure, meaning it always has a specific makeup or composition and a specific set of properties. Physical property: characteristic of a pure substance that can be observed without changing it into another substance. Chemical property: characteristic of a pure substance that describes its ability to change into a different substance. Element: pure substance that cannot be broken down into any other substances by chemical or physical means. Atom: basic particle from which all elements are made. Chemical bond: force of attraction between two atoms. Molecules: groups of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. Compound: pure substance made of two or more elements chemically combined in a set ratio. Chemical formula: shows the elements in the compound and ratio of atoms. Mixture: made of two or more substances (elements or compounds, or both) that are together in same place but are not chemically combined. Heterogeneous mixtures: mixture in which pure substances are unevenly distributed throughout the mixture. Homogeneous mixture: mixture in which substances are evenly distributed throughout the mixture Solution: well-mixed mixture containing a solvent and at least one solute that has the same properties throughout. Solute: part of a solution present in a lesser amount and dissolved by the solvent Solvent: part of a solution that is present in the largest amount and dissolves a solute. 1. Properties of Matter a. Matter can have many different properties or characteristics. i. They can be hard or soft, rough or smooth, hot or cold, liquid, solid, or gas. ii. Some materials catch fire easily, while others do not burn b. The properties and changes of any type of matter depend on its makeup c. Some types of matter are substances, and others are not. d. Is table salt a substance? Explain. i. _________________________________________________________________________________ e. Is the batter for blueberry muffins a substance? Explain. i. _________________________________________________________________________________ f. Every form of matter has two kinds of properties, physical properties and chemical properties i. These properties are used to classify matter ii. Oxygen 1. Chemical property ___________________________________________________ 2. Physical property ____________________________________________________ Physical Property i. Examples: 1. __________________ 2. __________________ 3. __________________ 4. __________________ 5. __________________ h. Chemical Properties i. To observe these properties you must try to change it into another substance (matter must be undergoing a chemical reaction) ii. Examples: 1. _________________________ 2. _________________________ 3. _________________________ Elements a. What is an element? i. All matter in the universe is made of slightly more than 100 elements ii. ______________ are the simplest substances 1. They can be identified by their specific chemical and physical properties g. 2. b. iii. Examples: 1. _____________ 2. _____________ Particles of elements-atoms i. All elements are composed of tiny atoms ii. Elements have different properties because their atoms are different 1. Contain different numbers of protons, neutrons, and electrons 2. _____________ is the center of the atom a. Contains _______________ and _____________ b. Has a ________________ charge c. 3. 4. When atoms combine i. Atoms of must elements have the ability to combine with other atoms, they form chemical bonds. ii. When atoms combine they form larger particles called molecules 1. Examples: Compounds (when elements combine) a. Most elements in nature are found combined with other elements i. When they are chemically combined in a set ratio they are called __________________. ii. When elements are chemically combined, they form compounds having properties that are different from those of the uncombined elements. 1. The ratio of elements in a compound is shown by a chemical formula a. A subscript after the element’s symbol tells the ratio of that element in the compound b. Example: c. Explain_______________________________________________________ Mixtures a. Elements and compounds are pure substances, but most of the materials you see everyday are not. Instead they are mixtures. b. Each substance in a mixture keeps its individual properties (because they are not chemically bonded). c. They are also not combined in a set ratio i. Heterogeneous mixture 1. You can see the different parts ii. Homogeneous mixture 1. So evenly mixed that you can’t see the different parts a. A solution is a kind of homogeneous mixture iii. Are the following heterogeneous or homogeneous mixtures 1. Soil- ____________________________ 2. Salt water- ______________________ 3. Kool-Aid- ________________________ 4. Salad- __________________________ d. Separating a Mixture i. A compound can be difficult to separate, but a mixture is usually easy to separate into its components because each component keeps its own properties. ii. Why would the following techniques be used to separate a mixture (what properties)? 1. Using magnets 2. Filtration 3. Distillation 4. Evaporation