Supplementary Information (docx 569K)
advertisement

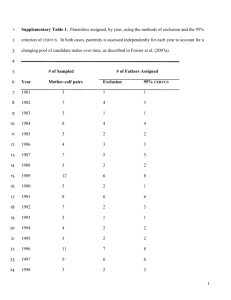
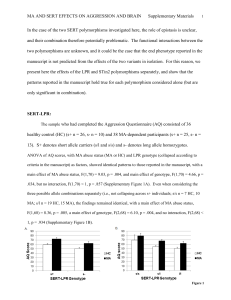
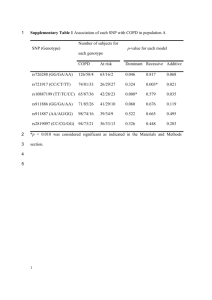
Supplementary Information for “Whole genome association analysis of treatment response in obsessive-compulsive disorder” The OCD Collaborative Genetics Association Study Corresponding to: Yin Yao Shugart, Building 35, Room 3A1000, 35 Convent Drive MSC3726, Unit on Statistical Genomics, Division of Intramural Research Programs, National Institute of Mental Health, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA, Telephone: 301-496-4341, Fax: 301-480-0673, E-mail:yin.yao@nih.gov This supplementary data file includes the illustration of genes enriched in glutamatergic system and serotonergic system (Supplementary Figure S1); and the results of power calculation (Supplementary Figure S2). 1 Supplementary Figure S1. Illustration of genes enriched in glutamatergic system and serotonergic system. (a) The serotonin signaling pathway. (b) The glutamate signaling pathway. Note: the ovals indicate the molecules in the synaptic transmission. The brown ovals were used to highlight the genes with p-value <0.001. 2 Supplementary Figure S2. Power calculation for genetic association analyses. The power for the association test was calculated at type I error rate of 0.05 using the sample size of this study (responders/non-responders = 514/290). Power calculation was conducted under the additive model, in which the genotype relative risk (GRR) for the “Aa” genotype ranges from 1.25 to 3, and the GRR for “AA” genotype ranges from 2.5 to 6, respectively. Phenotype prevalence was set at 0.03. We explored the high risk allele frequency (A) ranging from 0.1 to 0.3, and the marker allele frequency (B) was equal to allele A, assuming that A and B allele are in strong LD (D-prime = 0.8). 3