Lecture Outline - Tissues
advertisement
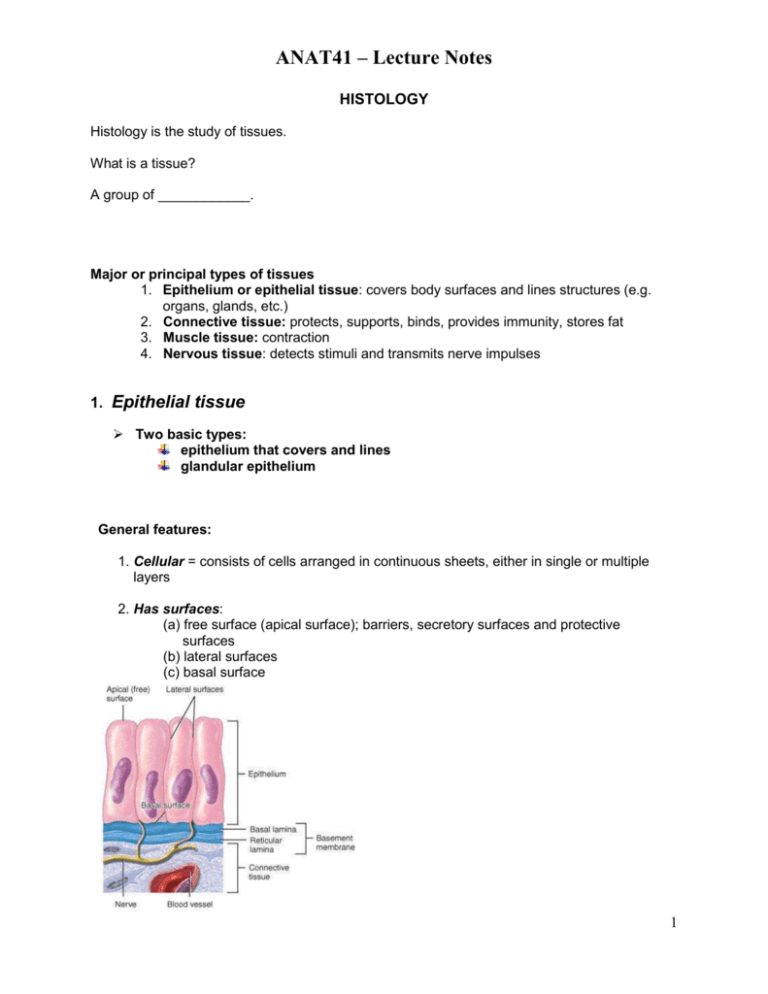
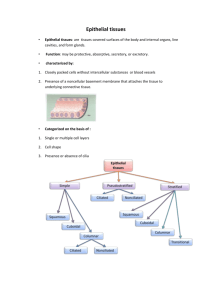
ANAT41 – Lecture Notes HISTOLOGY Histology is the study of tissues. What is a tissue? A group of ____________. Major or principal types of tissues 1. Epithelium or epithelial tissue: covers body surfaces and lines structures (e.g. organs, glands, etc.) 2. Connective tissue: protects, supports, binds, provides immunity, stores fat 3. Muscle tissue: contraction 4. Nervous tissue: detects stimuli and transmits nerve impulses 1. Epithelial tissue Two basic types: epithelium that covers and lines glandular epithelium General features: 1. Cellular = consists of cells arranged in continuous sheets, either in single or multiple layers 2. Has surfaces: (a) free surface (apical surface); barriers, secretory surfaces and protective surfaces (b) lateral surfaces (c) basal surface 1 ANAT41 – Lecture Notes 3. Avascular - no blood supply 4. Innervated - has nerve supply 5. Mitotically active - cells divide to produce a new population Epithelium is classified based on the cell shape and number of layers. Layers: Simple vs. Stratified Basic Shapes: Squamous - thin, flattened cells (resembles a fried egg) Cuboidal - equal widths and lengths, cube or hexagon shaped Columnar - taller than they are wide 2 ANAT41 – Lecture Notes Types of Epithelium Simple squamous Characteristics Location Function Single layer of flat cells, with a centrally located nucleus Lines heart, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, air sacs of lungs, capsule of kidney, serous membranes Filtration, diffusion, secretion, osmosis Single layer of cubed shaped cells, with a centrally located nucleus Covers surface of ovary, lines cornea, forms pigmented area of retina, lines kidney tubules, small ducts and glands Secretion and absorption Single layer of columnar shaped cells, with basally located nucleus; can be ciliated or non-ciliated Non-ciliated: Lines GI tract, ducts of many glands, gallbladder Ciliated: Bronchioles, uterine tubes, uterus, central canal of spinal cord, ventricle of brain Secretion and absorption Several layers of cells,with varying shapes; apical cells are squamous shaped Epidermis of skin, Lining of mouth, esophagus, part of epiglottis, part of pharynx, vagina, and tongue Protection Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Moves mucus and other substance s by ciliary action Stratified squamous 3 ANAT41 – Lecture Notes Stratified cuboidal Typical two or layers of cubed shaped cells; can be more than 2 Ducts of sweat glands, esophageal glands, and parts of male urethra Protection , and some secretion and absorption Several layers of cells, only the apical looks columnar shaped Parts of urethra, excretory ducts of some glands, anal mucous membrane, part of the conjunctiva of the eye Protection and secretion Only 1 cell layer thick, but has the appearance of multi-layers because the nuclei of the cells lie at different levels Ciliated: Lines airways of the respiratory tract Non-ciliated: large glands, epididymis, parts of male urethra Secretion and movement of mucus by cilia Lines urinary bladder, parts of ureters, and urethra Allows for distention or stretching Stratified columnar Ciliated Pseudostratified columnar Transitional Has several layers, but there is transitional shapes of cells from cuboidal to squamous; apical layer has dome shaped cells that may be binucleated 4 ANAT41 – Lecture Notes Glands = function in secretion; one or more specialized cell types that release their contents into ducts, onto a surface or directly into the blood. Classified as either exocrine or endocrine. a. exocrine =Secrete their products into ducts and onto body surfaces or cavities Examples: b. endocrine = Secrete their products directly into the blood Examples: 2. Connective Tissue (CT) General characteristics: Ground substance Protein fibers (3 types) Collagen Elastic Reticular Specialized cells Ground substance + protein fibers = extracellular matrix Types of Cells found in connective tissue: 1. Fibroblasts 2. Macrophages 3. Plasma cells 4. Mast cells 5. Adipocytes 5 ANAT41 – Lecture Notes Types of Loose Connective Tissue Areolar Adipose Reticular Types of Dense Connective Tissue Dense regular Characteristics Location Contains all 3 types of fibers, several kinds of cells; most predominant type of connective tissue proper in the body Subcutaneous layer of skin, papillary layer of dermis, lamina propria of mucous membranes, around blood vessels, nerves, body organs Subcutaneous Adipocytes that layer of the skin, store lipids; the around heart and cytoplasm and kidneys, yellow nucleus are pushed bone marrow, to the periphery by padding around lipid droplet joints and sockets of the eye Network of reticular Liver, spleen, fibers and cells lymph nodes, red bone marrow, around bloods vessels and muscle Function Strength, elasticity and support Reduces heat loss, energy storage, supports, and protects Characteristics Location Forms stroma of organs, binds smooth muscle, filters and removes worn out blood cells Function Collagen fibers densely arranged, with fibroblasts between them Tendons, ligaments, aponeuroses Provides strong attachments 6 ANAT41 – Lecture Notes Dense irregular Elastic Densely packed, randomly arranged collagen fibers Fasciae, Reticular layer of the dermis, Fibrous pericardium of heart, periosteum of bone, perichondrium of cartilage, joint capsules, membrane around many organs, heart valves Provides strength Densely packed elastic fibers, with fibroblasts between them Lung tissue, walls of elastic arteries, trachea, bronchiole tubes, true vocal cords, suspensory ligaments of the penis, ligaments between vertebrae Allows stretching of various organs Types of Supportive Connective Characteristics Tissue Hyaline Cartilage Chondrocytes in lacuna, "glassy" like matrix that resembles a water picture Location Function Ends of long bones, anterior ends of ribs, parts of larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchiole tubes, embryonic Smooth surface for articulating structures, support, and flexibility 7 ANAT41 – Lecture Notes tissue, and fetal skeleton Elastic Cartilage Chondrocytes in a lacuna, with elastic fibers in the background, appears "dirty" Fibrocartilage Bone Chondrocytes in the lacuna that are arranged in rows, wave like collagen in the matrix System of osteons, with features that include lamellae, lacunae, osteocytes, canaliculi and haversian canal Types of Fluid Connective Characteristics Tissue Blood Consists of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets Epiglottis, Ear, Auditory or Eustachian tube Support and maintain shape Pubic symphysis, Intervertebral discs, menisci of the knee Support and fusion Compact and spongy bones of the skeletal system Support, protection, storage, houses blood forming tissues, aids in movement Location Function Within bloods vessels, and chambers of the heart Transports, phagocytosis, involved in allergic reactions, immune response and blood clotting 8 ANAT41 – Lecture Notes 3. Muscle Tissue General functions: Produces body movements Generates heat Maintains posture There are 3 different types of muscle tissue: 1. Skeletal (voluntary or striated) muscle: parallel fibers, multi-nucleated, striated Location: 2. Smooth (visceral) muscle: spindle shaped cells, with a centrally located nucleus; involuntary Location: 3. Cardiac muscle: Branched cells, with centrally located nuclei, striated; involuntary Location: 9 ANAT41 – Lecture Notes 4. Nervous Tissue A. Neuron or nerve cells = send and receive messages What is the basic structure? Location: brain, spinal cord, nerves B. Neuroglia = support and nourish nervous tissue Location: brain, spinal cord only Membranes - combination of epithelial and connective tissue Definition: a sheet of tissue which lines a body cavity or covers a body surface Types of membranes: Epithelial membranes 1. Mucous membranes - lines body cavities that open to the exterior 2. Serous membranes - has two parts: parietal and visceral layers line body cavities and covers the organ that lie within the cavities 3. Synovial membrane - lines cavities of the joints 3. Cutaneous membrane (skin) - We'll talk about this one in more detail In the next chapter. 10