Chapter 05
advertisement

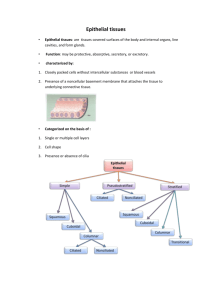
Biology 112 Chapter 5: Tissues Epithelial Tissue (epithelium): a sheet of cells that lines a body cavity or covers a body surface covering & lining epithelium: skin & lining of body cavities glandular epithelium: forms glands many functions: protection, absorption, secretion, excretion, filtration, sensory reception capable of regeneration epithelial tissue is avascular basement membrane: anchors epithelium to underlying connective tissue; part of extracellular matrix Classification of Epithelia: squamous (flattened), cuboidal (cube-shaped), & columnar (columnshaped) cells simple (1 layer) or stratified (multiple layers) Simple Squamous Epithelial Tissue: single layer of flattened cells with discshaped nuclei & little cytoplasm locations: in kidney glomeruli, air sacs of lungs, heart lining, blood vessels & lymphatic vessels, lining of ventral body cavity functions: diffusion & filtration; secretes lubricating substances in serosae Simple Cuboidal Epithelial Tissue: single layer of cube-shaped cells with large spherical nuclei; often seen in circular pattern when cut in cross section locations: in kidney tubules, ducts of small glands, ovary surface functions: secretion & absorption Simple Columnar Epithelial Tissue: single layer of column-shaped cells with oval nuclei; some have cilia or microvilli; may include goblet cells locations: nonciliated in most of digestive tract, gallbladder & excretory ducts of some glands; ciliated in small bronchi, some regions of uterus functions: absorption, secretion of mucus, enzymes...; ciliated propels mucus, reproductive cells Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelial Tissue: single layer of mostly columnshaped cells with different heights (some don't reach apical surface) & nuclei at different levels; some have cilia; may include goblet cells 1 locations: nonciliated in male sperm-carrying ducts & ducts of large glands; ciliated type lines trachea & most of upper respiratory tract functions: secretion & propulsion of mucus Stratified Squamous Epithelial Tissue: multiple layers; basal layer cuboidal or columnar - carry out metabolism & mitosis; outer layers are keratinized locations: nonkeratinized in most of digestive tract, gallbladder & excretory ducts of some glands; keratinized in epidermis of skin functions: protects underlying tissues Stratified Cuboidal Epithelial Tissue: several layers – lines lumen of ducts/tubes locations: ovarian follicles, seminiferous tubules & some large ducts of glands (mammary, sweat, salivary, pancreatic) functions: protection, secretion Stratified Columnar Epithelial Tissue: several layers - basal layer usually cuboidal locations: male urethra & vas deferens; parts of pharynx functions: protection, secretion Transitional Epithelial Tissue: several layers - basal layer cuboidal or columnar; surface cells dome-shaped or squamous-like (depending on stretch) locations: ureters, bladder & part of urethra functions: stretches & distends urinary organ Glandular Epithelial Tissue Gland: 1 or more cells that produce & secrete a specific product - unicellular or multicellular Endocrine glands: release product into extracellular space - ductless glands... eventually lose their ducts Exocrine glands: release product to an epithelial surface includes mucus, sweat, oil, & salivary glands merocrine glands: secrete product by exocytosis ● serous cells: secrete watery fluid with enzymes called serous fluid ● mucous cells: secrete mucus, containing the glycoprotein mucin goblet cells: serve protective function in gastrointestinal & respiratory tracts apocrine glands: lose small portions of gland during secretion holocrine glands: accumulate product until gland ruptures Connective Tissue: most abundant primary tissue 2 connective tissues bind structures, provide support & protection, serve as frameworks, fill spaces, store fat, produce blood cells, protect against infections & help repair tissue damage cells in connective tissue are varied and usually divide range of vascularity, but most have good blood supplies extracellular matrix (collagen or elastin fibers; calcium phosphate (bone) ground substance: fills space between cells & contains fibers Connective Tissue Cells: fibroblasts (many types) chondrocytes (cartilage) & osteocytes (bone) white blood cells, mast cells, macrophages (blood,...) Connective Tissue Fibers: collagen: thick fibers (of collagen protein); provide tensile strength (resist tension) elastic: thin fibers made of elastin protein; stretch easily reticular: very thin collagenous fibers; lend delicate support (lymphoid tissues) Connective Tissue Types: Areolar (Loose) Connective Tissue: gel-like matrix with all 3 fiber types; fibroblasts, mast cells, macrophages & some white blood cells location: under many epithelia (forms lamina propria); around organs & capillaries functions: cushions organs; many immune cells regulate immunity Adipose Connective Tissue: closely packed adipocytes (fat cells with large fat droplet) location: under skin, around kidneys & eyeballs, within abdomen, breasts functions: cushions organs; reserve food fuel, insulation Dense Connective Tissue: dense (primarily) parallel collagen fibers, few elastin fibers; fibroblasts location: tendons, ligaments, dermis of skin, digestive submucosa, fibrous capsules of organs & joints functions: attaches muscles to bone & other muscles, attaches bones to bones; withstands high stress; adds structural strength Cartilage: mostly water; no blood vessels or nerves surrounded by a layer of dense irregular connective tissue - the perichondrium, which contains blood vessels 3 contains chondrocytes in lacunae, ground substance & fibers 3 types: hyaline, elastic & fibrocartilage hyaline cartilage: amorphous firm matrix; collagen fibers form glassy (invisible) network; chondrocytes in lacunae ● location: embryonic skeleton, covers long bones in joints, costal cartilage of ribs, cartilage of nose, trachea & larynx ● functions: support, cushioning, resists stress elastic cartilage: similar to hyaline cartilage, with elastin fibers in matrix ● location: external ear (pinna), epiglottis ● functions: maintains shape while adding flexibility fibrocartilage: similar to hyaline, less firm with thick collagen fibers in matrix ● location: intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, knee joint discs ● functions: tensile strength, absorbs shock Bone: hard calcified matrix, many collagen fibers, well-vascularized, osteocytes in lacunae location: bones functions: support, levers for muscles, calcium storage, blood cell formation (hematopoiesis) in marrow Blood: red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes) & platelets in fluid matrix (plasma) location: in blood vessels functions: transports oxygen & carbon dioxide, nutrients, wastes & other substances Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Muscle: multinucleate, long cylindrical cells with peripheral nuclei; striated; voluntary muscle location: attached to bones of skeleton function: contraction helps move bones Smooth Muscle: uninucleate, spindle-shaped cells; centrally located nucleus; nonstriated; involuntary muscle location: lines hollow passageways such as: walls of blood vessels, airways to lungs, stomach, intestines & bladder function: contraction helps constrict or narrow lumen of blood vessels, break down & move food through GI tract, move fluids & eliminate wastes Cardiac Muscle: one centrally located nucleus (usually); striated; branched; intercalated discs (desmosomes & gap junctions) between cells location: myocardium of heart 4 function: contraction helps propel blood from heart to tissues Nervous Tissue: neurons & neuroglial cells (supporting cells) location: brain, spinal cord & nerves functions: transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors to effectors Types of Membranes: serous: fluid membrane surrounding organs... pleura (lungs), pericardium (heart), peritoneum (digestive organs) ● visceral & parietal mucous: lines body cavities (digestive tract, respiratory tract) ● specialized cells (glands) may secrete mucus cutaneous (epithelial): skin synovial membranes: line cavities of freely movable joints areolar CT with elastic fibers & adipocytes 5