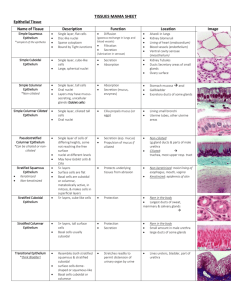
Tissues
Function and Location
For Epithelial, Connective, Muscular
and Nervous
Nervous tissue: Internal communication
• Brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Muscle tissue: Contracts to cause movement
• Muscles attached to bones (skeletal)
• Muscles of heart (cardiac)
• Muscles of walls of hollow organs (smooth)
Epithelial tissue: Forms boundaries, protects,
secretes, absorbs, filters
• Skin surface (epidermis)
• Lining of GI tract organs and other hollow organs
Connective tissue: Supports, protects, binds
• Bones
• Tendons
• Fat and other soft padding tissue
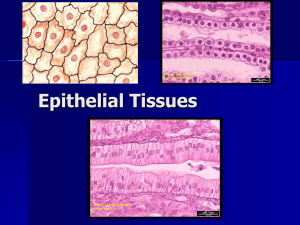
Characteristics of All Epithelial
• Composed mainly of cells bound closely together
• A free surface exposed to the environment,
passageway or internal chamber
• Basement membrane
• Avascular
• Regeneration
• May have villi, microvilli or cilia
Functions of Epithelial Tissue
• Physical Protection
– Intercellular connections/gap junctions and tight
junctions
• Control Permeability
• Provide Sensation
• Produce specialized secretions
– Exocrine – secretions are discharged unto the
surface or through duct
• i.e. sweat, milk
– Endocrine – secretions are released into blood
stream
• i.e. hormones
Classifying Epithelial
• Classified by number of cell layers
– Simple – one cell layer
– Stratified – more than one layer of cells
• And Cell shape
– Squamous – cells are thin and flat,
– Cuboidal – small boxes, appear square, nucleus
lies near center of cell
– Columnar – column like cells with oval nuclei.
– (Shape of nucleus is similar to shape of cell.)
Simple Squamous
C: flattened cells; fried egg appearance
F: thin, permeable, used for filtration/absorption
by diffusion
LOCATIONS: lines heart and blood vessels,
Covers organs, portions of kidney tubules;
cornea; alveoil of lungs
FUNCTIONS: Reduces friction;
controls vessel permeability;
performs absorption and secretion
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Connective tissue
Lining of peritoneal cavity
Simple Cuboidal
C: one layer of cube-like cells w/ large spherical central nuclei
F: secretion and absorption
L: glands, ducts, portions of kidney tubules
LOCATIONS: Glands; ducts;
portions of kidney tubules; thyroid
gland
Connective
tissue
FUNCTIONS: Limited protection,
secretion, absorption
Nucleus
Kidney tubule
Cuboidal
cells
Basement
membrane
Simple Columnar
(c) Simple columnar epithelium
C: single layer of tall closely packed cells; oval nucleus;
may cilia and goblet cells. Goblet cells secrete mucus.
F: absorption and secretion; some can hold and secrete
mucus, enzymes
L: digestive tract, uterine tubes, c. ducts of kidneys
Microvilli
LOCATIONS: Lining of
stomach, intestine, gallbladder,
uterine tubes, and collecting
ducts of kidneys
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Intestinal lining
FUNCTIONS:
Protection,
secretion,
absorption
Basement
membrane
Loose
connective
tissue
(c) Simple columnar epithelium
Description: Single layer of tall cells
with round to oval nuclei; some cells
bear cilia; layer may contain mucussecreting unicellular glands (goblet cells).
Simple
columnar
epithelial
cell
Function: Absorption; secretion of
mucus, enzymes, and other substances;
ciliated type propels mucus (or
reproductive cells) by ciliary action.
Location: Nonciliated type lines most of
the digestive tract (stomach to anal canal),
gallbladder, and excretory ducts of some
glands; ciliated variety lines small
bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions
of the uterus.
Photomicrograph: Simple columnar epithelium
of the stomach mucosa (860X).
Basement
membrane
• Simple Columnar in
the Digestive Tract
• Goblet Cells
• Cilia
Pseudostratified Columnar
C: One layer of cells with varying heights; nuclei seen at different
levels; may have goblet cells (secrete) and have cilia
F: secrete mucus primarily
L: lining of nasal cavity, bronchi and trachea
Pseudostratified from trachea
LOCATIONS: Lining of
nasal cavity, trachea, and
bronchi; portions of male
reproductive tract
Cilia
Cytoplasm
Nuclei
FUNCTIONS:
Protection,
secretion
Basal lamina
Trachea
Loose
connective
tissue
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
C: free surface cells are squamous; deeper layers are
cuboidal
F: protection against abrasion, pathogens,chemical attack
L: surface of skin, extends into every opening
LOCATIONS: Surface of skin;
lining of mouth, throat, esophagus,
rectum, anus, and vagina
FUNCTIONS: Provides physical
protection against abrasion,
pathogens, and chemical attack
Squamous
superficial cells
Stem cells
Basal lamina
Connective
tissue
Surface of tongue
Generally 2 layers of cube-like cells
Function: Protection
Location: sweat glands and other large glands
LOCATIONS: Lining of some
ducts (rare)
Lumen
of duct
FUNCTIONS: Protection,
secretion, absorption
Stratified
cuboidal
cells
Basal
lamina
Sweat gland duct
Nuclei
Connective
tissue
Transitional Epithelium
C: resembles both stratified cuboidal and stratified squamous; basal cells resemble
columnar or cuboidal; surface cells similar to squamous
F: stretch and recoil
Description: Resembles both
stratified squamous and stratified
cuboidal; basal cells cuboidal or
columnar; surface cells dome
shaped or squamouslike, depending
on degree of organ stretch.
Transitional
epithelium
Function: Stretches readily and
permits distension of urinary organ
by contained urine.
Location: Lines the ureters, urinary
bladder, and part of the urethra.
Basement
membrane
Connective
tissue
Photomicrograph: Transitional epithelium lining the urinary
bladder, relaxed state (360X); note the bulbous, or rounded,
appearance of the cells at the surface; these cells flatten and
become elongated when the bladder is filled with urine.
LOCATIONS: Glands; ducts;
portions of kidney tubules; thyroid
gland
FUNCTIONS: Limited protection,
secretion, absorption
Connective
tissue
Nucleus
Cuboidal
cells
Basal
lamina
Kidney tubule
LOCATIONS: Lining of some ducts
(rare)
Lumen
of duct
FUNCTIONS: Protection, secretion,
absorption
Stratified
cuboidal
cells
Basal
lamina
Nuclei
Connective
tissue
Sweat gland duct
LOCATIONS: Urinary
bladder; renal pelvis;
ureters
FUNCTIONS: Permits
expansion and recoil
after stretching
Epithelium
(relaxed)
EMPTY BLADDER
Basal lamina
Connective tissue
and smooth
muscle layers
Epithelium
(stretched)
Basal lamina
FULL BLADDER
Urinary bladder
Connective tissue
and smooth
muscle layers
Glandular Epithelium
Two types:
Endocrine – ductless; secrete hormones into
extracellular space; eventually enters blood
stream.
Exocrine – more numerous; secrete products
using ducts
i.e sweat, oil, mucus, enzymes
Classified by structure, mode and type of
secretion.
Unicellular Exocrine glands
• Ductless
• Goblet cells
secrete mucus
directly into
organ; mucus
never makes it to
bloodstream
Merocrine Glands
Secrete products by exocytosis
Cells aren’t changed after
secretion
i.e pancreas, sweat glands,
salivary glands
Apocrine Glands
Accumulate products underneath cell
surface; eventually cell pinches off
Cell repairs itself; repeats process
I.e. mammary glands, sweat glands under
arm pits
Holocrine Glands
Oil gland
Accumulate product until they
rupture “die for cause”
Secretions include product plus
cell debris
i.e. sebaceous (oil) glands
Secretory
vesicle
Golgi
apparatus
Nucleus
Salivary gland
Merocrine
Breaks
down
Mammary
gland
Golgi apparatus
Secretion
Regrowth
Apocrine
Cells burst,
releasing cytoplasmic
contents
Hair
Sebaceous
gland
Cells produce
secretion, increasing
in size
Hair follicle
Cell division replaces
lost cells
Holocrine
Stem cell
Functions of Connective Tissue
•
•
•
•
Binding, support and protection
Insulation/Storing Energy
Defending the body
Transportation of substances
Characteristics of Connective
Tissue
• Common origin – all arise from same
embryonic tissue: Mesenchyme (next slide)
• Degree of vascularity
• Many Specialized cells
• Composed mainly of extracellular material;
not cells
– Matrix- includes fibers and ground substance
– Ground substance – fluid of tissue
Tissue types common origin
Mesenchyme
Common Origin
Fibroblasts
Connective Tissue Proper
Chondroblasts
Form cartilage cells
Osteoblasts
Form bone cells
Hemocytoblasts
form blood cells
Blast: immature cell
Cyte: mature cell
Clast: cell that breaks down others. I.e. osteoclasts break down bone
Matrix
• Amorphous; has no distinct shape or form
• Ground substance – material that fills space
between cells; fluid of tissue
• 3 Types of fibers
– Collagen – long, straight, thick white fiber; strong
but flexible unbranched fiber
– Elastin – branched and wavy fiber that contains
protein elastin; coiled yellow fibers; rubberband
quality
– Reticular – least common; fine, branching fibers
that form networks of fibers; support soft tissue of
organs.
Connective Tissue
Cells of Connective Tissue Proper
• Fibroblasts- produce fibers and ground substance
• Macrophages – engulf bacteria and other foreign
bodies (phagocytize)
• Mast Cells – mark substances for destruction by
secreting chemicals (histamine) that start the
immune response
• Adipocytes (fat cells) – stores fat, nucleus and
organelles are pushed to the side.
Fixed
macrophage
Reticular
fibers
Mast cell
Melanocyte
Elastic
fibers
Plasmocyte
Free
macrophage
Blood
in vessel
Adipocytes
(fat cells)
Ground
substance
Collagen
fibers
Fibroblast
Free
macrophage
Mesenchymal
cell
Lymphocyte
C: loose matrix with all three fiber
types; contains macrophages, mast cells and WBC’s
F: cushion organs; phagocytize bacteria, (assists
when infections are present.
L: distributed under epithelia; packages organs
Elastic
fibers
Collagen
fibers
Fibroblast
macrophage
C: closely packed cells; nucleus pushed off to side by fat
droplet; vascular
F: reserve fuel; insulates; supports and protects organs.
L: under skin; around kidneys and eyeballs; in bones,
abdomen and breasts
LOCATIONS: Deep to the skin,
especially at sides, buttocks,
breasts; padding around eyes
and kidneys
FUNCTIONS: Provides
padding and cushions
shocks; insulates
(reduces heat
loss); stores
energy
Adipocytes
Adipose tissue
C: network of reticular fibers in lots of extracellular
matrix; composed of reticular cells and blood cells
F: form a soft internal skeleton for organs
L: lymph nodes; bone marrow and spleen
Reticular
fibers
Reticular tissue
C: mainly consists of parallel collagen and some elastin
fibers; main cell is fibroblast.
L: tendons and ligaments
F: Attach muscle to bone; bone to bone; withstands
pulling forces; (wavy fibers enable the tissue to stretch)
Collagen
fibers
Fibrocyte
nuclei
Tendon
Characteristics of Cartilage
• Avascular and lacks nerve
fibers (diffusion thus
cartilage is rarely thick)
• Ground substance
consists of chondroitin
sulfate
• Chondrocytes are the
working cells
• Lacunae (small cavities)
surround cells
C: matrix appears glossy (amorphous); collagen fibers most common;
but not visible
L: tip of nose trachea, larynx, rib’s costal cartilage, soft spot, bones of
synovial joints, and nasal septum
F: offers support with a little flexibility; absorbs; resists compressive
stress
LOCATIONS: Between tips of
ribs and bones of sternum;
covering bone surfaces at
synovial joints; supporting
larynx (voice box), trachea,
and bronchi; forming part of
nasal septum
Chondrocytes
in lacunae
FUNCTIONS: Provides
stiff but somewhat
flexible support;
reduces friction
between bony
surfaces
Matrix
Hyaline cartilage
C: little ground substance with lots of collagen fibers
dominating the matrix. Fibers are interwoven which
offers more strength
L: discs between vertebra, pubic symphysis, knee meniscus
F: shock absorber, resist compressions, prevents bone to bone
contact.
Collagen
fibers in
matrix
Chondrocyte
in lacuna
Fibrous cartilage
C: contains more elastin fibers making tissue very flexible
L: ear, epiglottis
F: maintains shape of structure but offers more flexibility
and stretch.
Chondrocyte
in lacuna
Elastic fibers
in matrix
Elastic cartilage
C: matrix similar to cartilage but contains more collagen
fibers; ground substance is Ca and PO4; vascular, vessels
travel thru canaliculi; Lacunae (free space) may be present
F: support, protect, store Ca and PO4; forms blood cells
L: Bone
Canaliculi
Osteocytes
in lacunae
Central canal
Matrix
(k) Others: blood
Description: Red and white
blood cells in a fluid matrix
(plasma), proteins are not in fiber
Form but are dissolved in plasma,
Contains cell fragments called platelets
Function: Transport of
respiratory gases, nutrients,
wastes, and other substances.
Helps fight off disease, blood clotting
Location: Contained within
blood vessels.
Plasma
Neutrophil
Red blood
cells
Lymphocyte
Photomicrograph: Smear of human blood (1860x); two
white blood cells (neutrophil in upper left and lymphocyte
in lower right) are seen surrounded by red blood cells.
Comparison of Classes of Connective Tissues (1 of 2)
Comparison of Classes of Connective Tissues (2 of 2)
Muscular Tissue
Characteristics
–
–
–
–
Contain many cells
Contains lots of vascular tissue
Elongated shape; cells are called fibers
Possess myofilaments, proteins that enable the
muscle to contract.
C: long parallel cells with many nuclei; banded or
striated; voluntary
L: attach to bones of skeleton
F: large movements; walking, moving extremities
Nuclei
Muscle
fiber
Striations
Skeletal muscle
C: striated only one nuclei per cell; branching cells join at
junctions called intercalated discs; involuntary
F: intercalated disc enable to heart to beat as one unit.
Cardiac muscle contracts together and relaxes together.
L: walls of heart
Nucleus
Cardiac
muscle
cells
Intercalated
discs
Striations
Cardiac muscle
C: not striated; each cell contains one nucleus; fibers
appear to taper at ends; not exactly parallel; involuntary
F: moves substances through hollow organs
L: found in walls of digestive organs, urinary tract and
blood vessels
Smooth
muscle
cell
Nucleus
Smooth muscle
C: contains cells called neurons and supporting cells
F: neurons transmit electrical impulses; supporting cells are
nonconducting cells that support, insulate and protect neurons.
Nervous tissue
L: nervous
system: brain, spinal cord, nerves
Nuclei of
supporting
cells
Cell body
of a neuron
Neuron
processes
Photomicrograph: Neurons (350x)
Nuclei of neuroglia
Cell body
Axon
Dendrites
• Maintain physical structure
of tissues
• Repair tissue framework
after injury
• Perform phagocytosis
• Provide nutrients to neurons
• Regulate the composition of
the interstitial fluid
surrounding neurons
Nucleolus
Nucleus of neuron
Dendrites
(contacted by
other neurons)
Axon (conducts
information to
other cells)
Microfibrils and
microtubules
Mitochondrion
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Cell body (contains nucleus
and major organelles)
A representative neuron
(sizes and shapes vary widely)
Contact with
other cells