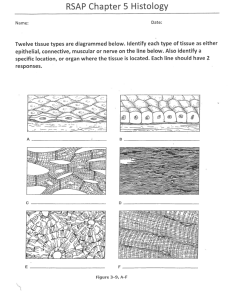
Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues
advertisement

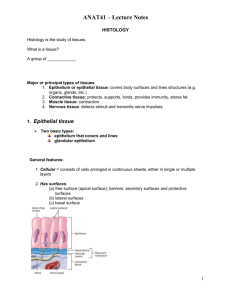
Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Anatomy of a Cell: 1)__________________ 2) _________________ 3)__________________ Nucleus: _____________________________ contains _____________________ -nuclear envelope is a barrier which contains pores that __________________________ -nucleoli is the site _________________________________ -chromatin is composed of _______________________________________ Cytoplasm: material outside of the nucleus ___________________________________ -Consists of 3 parts:________________________________________ -Organelles carry out specific functions. See worksheets for various types. Plasma membrane*: double _________________ layer, barrier for ___________ -Other materials embedded in the membrane(3): ________________________________ -purpose of cholesterol is to ________________________________________ -microvilli:______________________________________________________ Specializations: 1. Tight: __________, membranes fuse like a __________ *Structure: 2. Desmosomes: anchor __________________________ 3. Gap junctions: allows chemicals and __________________________ Cell Physiology Membrane transport:_________________________________________________________ Passive: ________________________ Diffusion: particles tend to _____________________________________ - move from a _____________ to a _______________ concentration - solute has to be ____________________ or __________ enough to pass through Types:simple diffusion: unassisted, particles are ____________ enough to fit through osmosis-______________________________________ Facilitated diffusion-requires a __________________ Active- transports substances unable to move by diffusion for the following reasons:__________ __________________________________________________________________________ Solute pumping: moves substances______________ the gradient, examples: ____________ Bulk transport Exocytosis: ___________________________________________________________ Endocytosis: __________________________________________________________ Phagocytosis: ____________________________ Pinocytosis:_________________________ 1. Isotonic have the ________________________________________ 2. Hypertonic is a solution that contains more ___________ in the cell than ______________ 3. Hypotonic is when there are _____________ solutes in the solution than in the ________ Cell Division Cells have 2 major periods: Interphase:__________________________________________ Cell Division:__________________________________________ Mitosis: division of ____________ whereas, cytokinesis is the _______________________ Steps in the phases: 1.________________-_____________ 2.________________-_____________ 3. ______________-_______________ 4.______________-________________ Gene: __________________________________________________________________ Some of proteins functions are __________________________________________________ Role of RNA Acts as a decoder for the DNA tRNA: ____________ amino acids to ribosome to build protein rRNA: helps form the _____________________________________________ mRNA: carries the instructions for _________________________________________ Transcription: ___________ of information from ______ base sequence to the complimentary base sequence of __________ Translation: base sequence of a _______________ is __________________________________ Tissues: Four types: 1. _________________ 2. ___________________3. _____________ 4. ________ Epithelial is found in body ____________ and ___________ also, _______________ tissue Function include: ________________________________________________________ Characteristics: -_________________________________ together - Tissues always have __________________________ - ____________________ (no blood supply) - regenerate _______________________ Draw what simple means: Draw what stratified means: ~Simple squamous: single layer of _____________ Forms membranes: examples of body parts it lines____________________ ~Simple cuboidal: single layer of __________________ Common in _______________________, found in ________________ and __________ ~Simple columnar: single layer of ______________ Cells usually produce ___________, typically found in ________________ ~Pseudostratified: single layer, but _____________________________ Ciliated such as in the _________________________ Functions: _______________ or ______________ ~Stratified squamous: cells __________________________ Locations: _________________________________________ ~Transitional epithelial: depends on _______________________ lines the _________________ Glands: one or more cells that _________________________________ Two types of glands develop from ____________________ 1. Endocrine: secretes __________________ and is ________________ 2. Exocrine: includes sweat and ________________ and has ducts Connective tissue is found ____________________ in the body Functions: 1.binds ____________________ 2. Supports ______________ 3. Provides ______ Characteristics: variations in ____________________ and _______________ nonliving material Why do you choose a broken bone over a torn ligament? ______________________________ (Matrix is everything but the cell; surrounding material + fibers) Types of Connective Tissue 1. Bone (______________): is used to __________________________________ -Composed of bones in cavities called _________________, a very hard ____________ _________________, and large numbers of _______________________. 2. Cartilage is less _______________ and more ___________ than _____________. a. Fetal skeleton is _________________, also found in the voice box and attaches the ribs -Composed of _________________________________ and ________________ b. Ear is made from _____________________ which provides ___________________ c. Fibrocartilage is not stretchy but highly ________________, forms discs in knee and 3. Dense connective tissue: main matrix is _________________________________. -Examples: ___________: muscles to ____________ Ligament: __________ to ______ Loose Connective Tissue 4. Areolar tissue: soaks up ________________ and causes an edema; “Glue” holds all organs in place. Contains many fibers through a loose network. 5. Adipose: cells contain _____________________________. -Functions: ___________ the body, ______________ some organs, _________________ -cell type: adipocytes (chicken wire appearance) 6. Reticular: _______________________________________________ -Forms a _________, which supports free blood cells. Found in _____________________ 7. Blood: surrounded by a ____________________________ called ____________. -Consists of protein fibers which are visible _________________. -_____________ nutrients, gases, and wastes throughout the body. Muscle Tissue are specialized to ____________ or __________ to produce _____________. 1. _____________ can be ____________, cells are ___________, attach to ______________ Have _______ nuclei. 2. _____________ found only in the ____________, cells attach to ____________________, functions involuntary, cells are ________________ and have _____ nucleus. 3. Smooth muscles are __________________, surround _____________________, attach to _______________, no striations and have ______ nucleus. An example ________________ Nervous Tissue consists of __________________________________________. -Functioning: _________________ and _______________ sends impulses to rest of body Tissue Repair or Wound Healing occurs by two methods: 1. Regeneration:___________________________________________________________ 2. Fibrosis:______________________________________________________________ Events: 1. Capillaries become _____________________ to ____________________________. 2._______________________________________ 3. Regeneration of __________________________________ __________________________: skin, bone, mucous membranes __________________________: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, nervous tissue (scars)