1st Quarter
advertisement

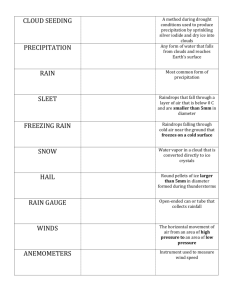
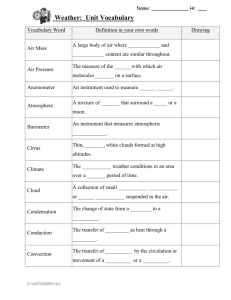
Quarterly Assessment Review (3rd quarter) 1. Aspect of Weather Temperature Tool Used to Measure it thermometer Unit of Measurement degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit Precipitation rain gauge inches Air Pressure barometer Cloud Cover None, direct visual observation Inches of mercury, millibars, other units as well % of sky covered Wind Direction *Direction the wind is coming from! Wind Speed Wind vane cardinal directions anemometer mph % (amount of water vapor in air compared to maximum capacity air can hold at that temperature) 2. Define weather: the conditions of the atmosphere such as temperature and precipitation at a particular time and place 3. Define climate: the average conditions of the atmosphere such as temperature and precipitation in a particular place over a long period of time Relative humidity psychrometer 4. The most important factor that influences climate: latitude 5. What heats faster/cools faster…land or water? _land____ Uneven heating of the Earth’s surfaces and air masses creates variations in temperature and air pressure. This causes air to move from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. This movement of air is known as __wind____. 6. What direction do the prevailing winds blow in our latitudes? ___west ________ to _____east_______ 7. Maritime air masses are moist air masses originating from the ___ocean________. Continental air masses are dry and originate over land. Polar air masses are cold air masses originating in the polar region. ____Tropical________air masses are warm because they originate in the tropics. 8. Describe three ways that clouds can form: 1. Heating and evaporation leading to water vapor rising, cooling and condensing into clouds. 2. When air masses meet, the warmer air is forced upward where the water vapor cools and condenses into clouds. 3. Landforms such as mountains can force air upward where the water vapor cools and condenses into clouds. 9. What can you expect if a cold front is coming in? Draw the symbol. Include the type(s) of cloud(s) associated with a cold front. You can expect cooler temperatures, cumulonimbus clouds and possible thunderstorms. 10. What can you expect if a warm front is coming in? Draw the symbol. Include the type(s) of cloud(s) associated with a warm front. You can expect warmer temperatures, increasing cloudiness, starting with cirrus, cirrostratus, altostratus, and finally nimbostratus clouds that produce long periods of rain. 11. What can you expect if a high pressure system is over you? Which direction do winds blow around a high pressure system? You can expect clearing or clear skies. Clockwise. 12. What can you expect if a low pressure system is over you? Which direction do winds blow around a low pressure system? You can expect cloudy skies. Counterclockwise. 13. When high and low pressure systems are far apart, winds blow from the area of high pressure to the area of low pressure slowly. When high and low pressure systems are close together, winds blow from the area of high pressure to the area of low pressure ___quickly_______. 14. Draw a station model using the following information: 39 degrees Fahrenheit, winds from the NW, barometric pressure 1019.4mb, 3/4 cloud coverage 15. Name the 5 different extreme weather events (guided notes handout): tornadoes, hurricanes, floods, droughts, thunderstorms (blizzards should be on the list too) 16. What is the name of the ranking scale for hurricanes? Saffir-Simpson scale It ranks hurricanes from category 1-5 based on the _wind speed_____, air pressure and storm surge. 17. The Fujita scale ranks __tornadoes_______ on a scale from 0 to 5 with 5 being the most severe. 18. What is the source of energy that powers the water cycle and severe weather events? the sun 19. Name the 4 layers of the atmosphere starting at the earth’s surface and going up: Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere 20. Name the layer of atmosphere where most of the weather occurs: Troposphere 21. Name the two main gases of the atmosphere and the percent of each of those parts: ____nitrogen____78% and ____oxygen_______ 21%. Argon and other trace gases including carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, make up the remaining portion along with water vapor and ozone which vary from location to location. 22. Which greenhouse gas is the greatest contributing factor to global warming? What is one man-made reason for the increase in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere? carbon dioxide, burning fossil fuels 23. Explain what the ozone layer does. It protects living organisms from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation from the _sun__ by absorbing those wavelengths of energy. 24. Know the basic steps or components of the water cycle, carbon/oxygen cycle, and nitrogen cycle. See all of your resources from earlier in the quarter, especially past quizzes/tests. 25. Water availability and distribution: Approximately what percentage of the world’s water is freshwater? 3% Approximately what percent of the world’s water is available for human use? 1% 26. Name one advantage and one disadvantage to drinking tap water rather than bottled water. Advantages: tap water is much cheaper than bottled water, tap water is checked and monitored more frequently for pollutants and test results are made available to the public, tap water produces much less trash/pollution. Disadvantages: tap water may be less pure than some bottled spring water, tap water may taste better to some people because it usually does not contain chlorine. 27. Which sector of society uses the most water? Is it agriculture, industry, or domestic (home) use? Which of the following types of foods require the most water to produce? Grains, fruits, vegetables, or meat? 28. What is one way you can conserve water or reduce the amount you use on a daily basis? You can take shorter showers, turn off the water while you brush your teeth, install low flow fixtures, consume less meat and dairy products, etc.