vocab flashcards
advertisement
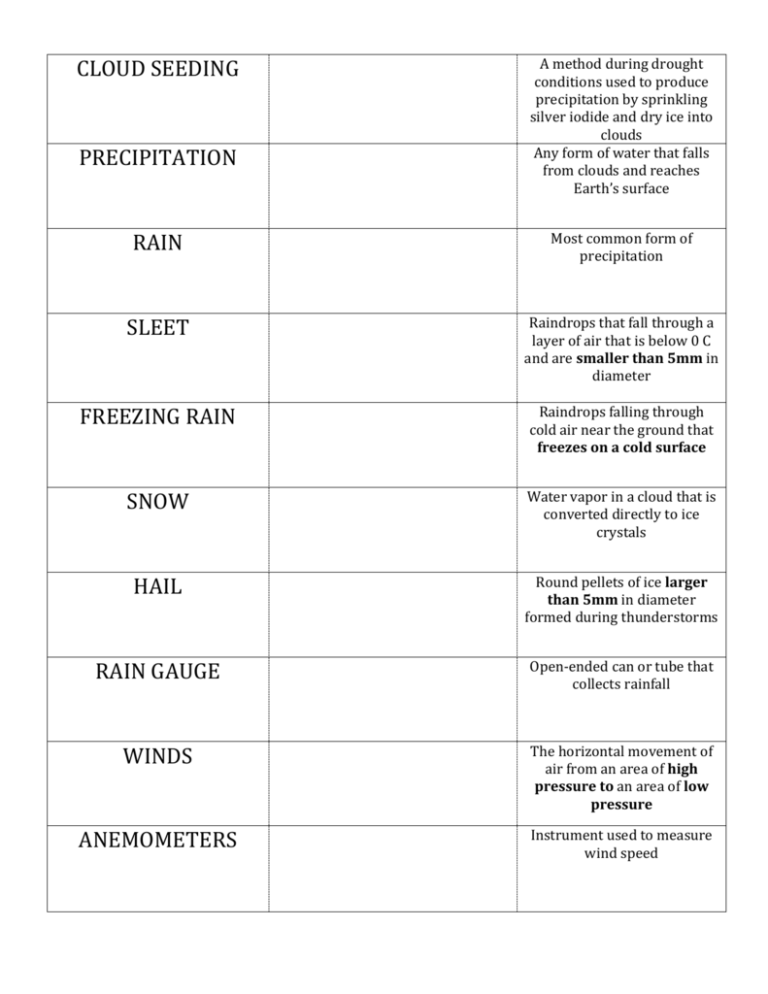
CLOUD SEEDING PRECIPITATION A method during drought conditions used to produce precipitation by sprinkling silver iodide and dry ice into clouds Any form of water that falls from clouds and reaches Earth’s surface RAIN Most common form of precipitation SLEET Raindrops that fall through a layer of air that is below 0 C and are smaller than 5mm in diameter FREEZING RAIN Raindrops falling through cold air near the ground that freezes on a cold surface SNOW Water vapor in a cloud that is converted directly to ice crystals HAIL Round pellets of ice larger than 5mm in diameter formed during thunderstorms RAIN GAUGE Open-ended can or tube that collects rainfall WINDS The horizontal movement of air from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure ANEMOMETERS Instrument used to measure wind speed TEMPERATURE The average amount of energy of motion of each particle in a substance CONDUCTION Heat transfer by objects in direct contact with each other CONVECTION Heat transfer by the movement of molecules in a fluid RADIATION Heat transfer without the objects coming in contact with each other WATER CYCLE The movement of water between the atmosphere and Earth’s surface (evaporation, condensation, &precipitation) EVAPORATION Process by which water molecules in liquid water escape into the air as water vapor HUMIDITY The measure of the amount of water vapor in the air RELATIVE HUMIDITY The percentage of water vapor that is actually in the air compared to the maximum amount of water vapor the air can hold Instrument used to measure relative humidity PSYCHROMETER FORMATION OF CLOUDS When water vapor in the air condenses to form liquid water or ice crystals ISOBARS Lines joining places on a weather map that have the same air pressure LOCAL WINDS Winds that blow over short distances LAND BREEZE Local winds that blow from the land to a body of water during the night SEA BREEZE Local winds that blow from an ocean or lake to the land during the day GLOBAL WINDS Winds that blow steadily from specific directions over long distances JET STREAMS Bands of high-speed winds about 10 km above the Earth’s surface AIR MASSES A huge body of air that has a similar temperature, humidity, and air pressure at any given height FOUR TYPES OF AIR MASSES 1.maritime tropical 2.continental tropical 3.maritime polar 4.continental polar FRONTS The boundary where two unlike air masses meet COLD FRONT When a fast-moving cold air mass takes over a warm air mass producing possible thunderstorms with heavy rains or snow WARM FRONT A warm air mass takes over a slow-moving cold air mass, produces humid, light rain or snow STATIONARY FRONTS When cold and warm air masses meet and neither can move the other OCCLUDED FRONTS When a warm air mass is caught between two cooler air masses WEATHER Condition of Earth’s atmosphere at a particular time and place ATMOSPHERE The envelope of gases that surrounds the planet TOPOSPHERE Layer where weather occurs STRATOSPHERE Layer where the ozone is located MESOSPHERE Layer that protects the Earth’s surface from being hit by meteoroids THERMOSPHERE The biggest and hottest layer (Ionosphere and Exosphere are part of this layer) IONOSPHERE Aurora Borealis (Northern Lights) are seen here EXOSPHERE Outermost layer of the atmosphere AIR PRESSURE A force resulting from the weight of a column of air pushing down on an area BAROMETER Instrument used to measure air pressure ALTITUDE Elevation or distance above sea level; as altitude increases, the density of the air decreases STORM A violent disturbance in the atmosphere THUNDERSTORM A small storm with heavy precipitation, thunder, and lightning that form in cumulonimbus clouds TORNADO A rapidly whirling, funnelshaped cloud that reaches down from a storm cloud to touch Earth’s surface TORNADO ALLEY The five states it crosses are: Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska, and Iowa TORNADO WATCH An announcement that tornadoes are possible in your area TORNADO WARNING An announcement that a tornado has been sighted and you should report to a storm shelter or the basement of a building HURRICANE A tropical cyclone that has winds of 119 km/h or higher STORM SURGE A “dome” of water that sweeps across the coast where a hurricane lands WINTER STORM A large amount of humid air that cools below 0 C can produce one METEROLOGIST A scientist who studies weather and tries to predict it