Water Cycle, Weather, and Clouds Study Guide
advertisement
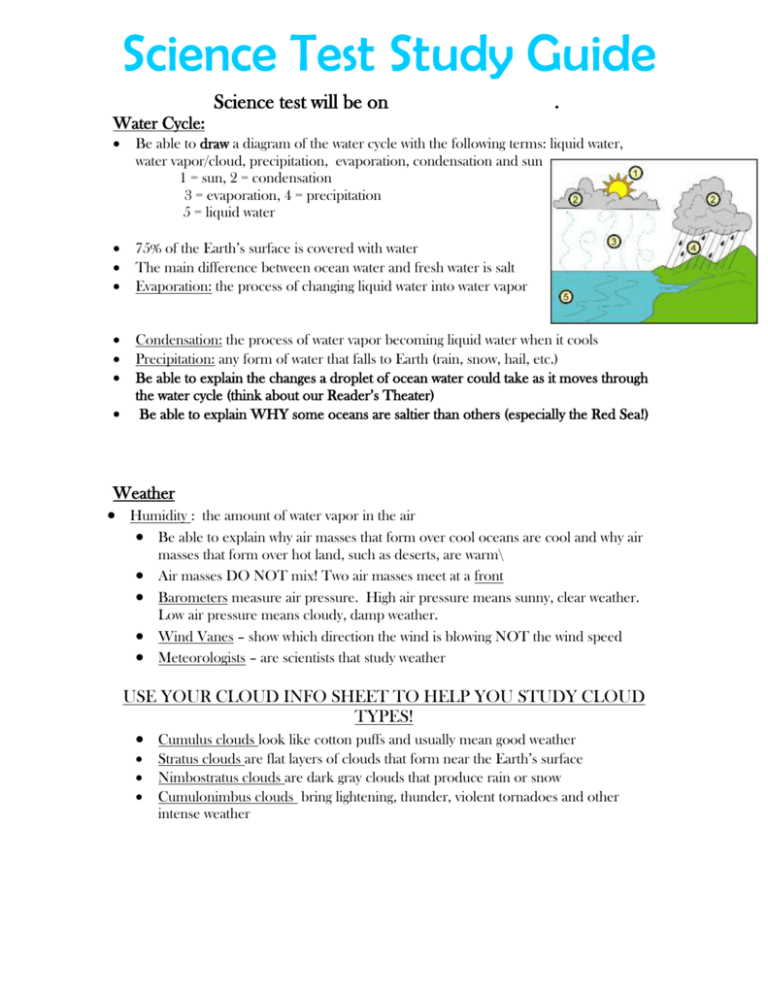
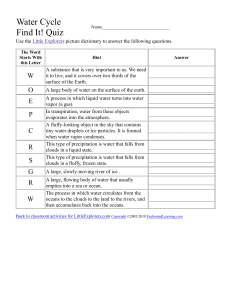
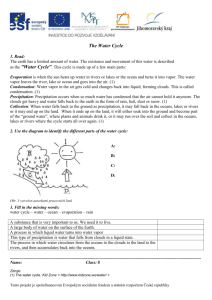
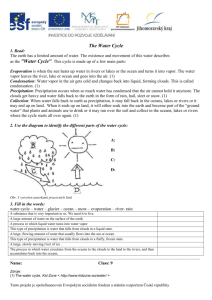
Science test will be on . Water Cycle: Be able to draw a diagram of the water cycle with the following terms: liquid water, water vapor/cloud, precipitation, evaporation, condensation and sun 1 = sun, 2 = condensation 3 = evaporation, 4 = precipitation 5 = liquid water 75% of the Earth’s surface is covered with water The main difference between ocean water and fresh water is salt Evaporation: the process of changing liquid water into water vapor Condensation: the process of water vapor becoming liquid water when it cools Precipitation: any form of water that falls to Earth (rain, snow, hail, etc.) Be able to explain the changes a droplet of ocean water could take as it moves through the water cycle (think about our Reader’s Theater) Be able to explain WHY some oceans are saltier than others (especially the Red Sea!) Weather Humidity : the amount of water vapor in the air Be able to explain why air masses that form over cool oceans are cool and why air masses that form over hot land, such as deserts, are warm\ Air masses DO NOT mix! Two air masses meet at a front Barometers measure air pressure. High air pressure means sunny, clear weather. Low air pressure means cloudy, damp weather. Wind Vanes – show which direction the wind is blowing NOT the wind speed Meteorologists – are scientists that study weather USE YOUR CLOUD INFO SHEET TO HELP YOU STUDY CLOUD TYPES! Cumulus clouds look like cotton puffs and usually mean good weather Stratus clouds are flat layers of clouds that form near the Earth’s surface Nimbostratus clouds are dark gray clouds that produce rain or snow Cumulonimbus clouds bring lightening, thunder, violent tornadoes and other intense weather