Section 3 and 4 - Revere Local Schools
advertisement

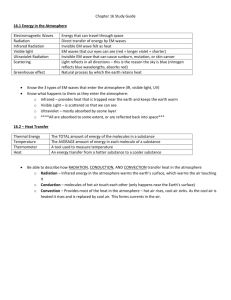
Chapter 2 sections 3 and 4 Study guide / notes Section 3 Wind Wind- wind is created by differences in air pressure (hot/cold) and the greater the pressure (temperature) difference, the greater the wind. Anemometer- an instrument used to measure wind speed. Wind Vane or Wind Sock- an instrument used to show wind direction Wind Chill Factor- the increased cooling caused by wind Local Winds- winds that blow over short distances and are created by the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface within a small area. Sea Breeze (lake breeze)- wind that blows from the ocean or lake toward the land. Usually occurs during the day time due to the cold air over the water wanting to chase out the warm air over the land. Land Breeze- Wind that blows from the land to the ocean or lake. Occurs at night due to the cold air over the land wanting to chase out the warm air over the water. Global Winds-winds that blow steadily from specific directions over long distances. They are created by the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface and occur over large areas. Doldrums- Area of little to know wind around the equator creating low pressure. Horse Latitudes- Dead air region located at 30o North and South Latitude. Sailors would get stuck in this region and have to throw their horses overboard. Trade Winds- region between the equator and 300 north and south latitude, where the winds generally blow from the east. Early sailors used these winds to bring trading goods to the West Indies. Prevailing Westerlies- located between 300 and 600 north and south latitude where the winds blow from the west. These winds play an important role in the weather patterns of the U.S. Polar Easterlies- Cold air region above 600 north and south latitude where the winds blow from the east. The polar easterlies factor greatly into the weather patterns of the United States. Jet Streams- about 10 kilometers above the Earth’s surface. They are bands of high speed winds, 200-400 kilometers per hour, that wander north and south. They blow from west to east. Coriolis Effect- The curving of wind/object in the atmosphere due to the rotation of the Earth. Section 4 Water in the Atmosphere Water Cycle- also known as the hydro cycle, is the 4 part movement of water between the Earth’s surface and the atmosphere. Evaporation- the process by which water molecules in liquid water escape into the air as water vapor. Condensation- the process by which water vapor cools and changes back into liquid water on condensation nuclei, thus forming clouds that we can see. Precipitation-Liquid water that falls from the sky in the form of rain, snow, sleet, and hail. Surface Runoff- is where the fallen precipitation is collected by the Earth’s surface in streams, rivers, lakes, and oceans. Humidity- the measure of the amount of water vapor in the air. Relative Humidity- the percentage of water vapor that is actually in the air compared to the maximum amount of water vapor the air can hold at a particular temperature. Psychrometer- an instrument used to measure relative humidity. Dew Point- temperature at which condensation begins. If the dew point is below freezing, it will create frost. Types of clouds Cirrus clouds- Wispy, feathery clouds that form at high altitudes. They are made of ice crystals. Cirrocumulus clouds (little rows of cotton balls) indicates that a storm is on the way. Usually form around 6 kilometers. Cumulus clouds- fluffy, rounded piles of cotton. The word cumulus means heap or masses. These clouds can form as low as 2 kilometers and extend up to 18 kilometers. The suffix “Nimbus” means rain. Stratus clouds- clouds that form in flat layers between 1-2 kilometers in the air. The word strato means spread out. They usually cover the entire sky and when they produce rain, they are called Nimbostratus. Altocumulus and Altostratus- the prefix “alto” means high. These are the clouds that are higher than cumulus and status, but lower than cirrus. Fog- Clouds that form at or near the ground. It often forms when the ground cools at night after a humid day. Fog is common near lakes, oceans, and mountains.