Cells and Organelles Review – Answers
advertisement

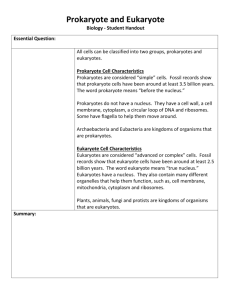
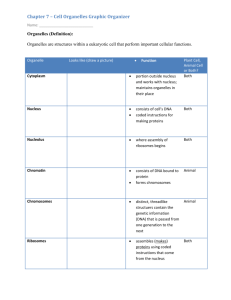
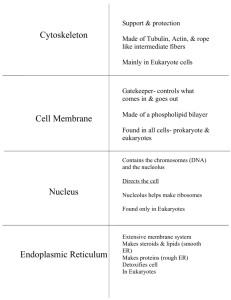
Name ________________________________________ Date _____________ Biology MCAS Prep Session 4: Cells and Organelles Today’s class will focus on questions that are hard because they are long and wordy, or because they involve interpreting graphs, charts, or diagrams. Do Now: Review from Past Classes! 1. What are the six most common elements in living things? Write the acronym (letters) and the name of each compound C – Carbon H – Hydrogen N – Nitrogen O – Oxygen P – Phosphorus S - Sulfur 2. Organic (carbon-based) compounds: Matching! __C___ lipids A. The building blocks of proteins B. Provides quick or long-term energy C. Provides waterproofing and forms cell membranes D. Building blocks of carbohydrates ___E__ nucleotides E. Building blocks of DNA and RNA __A___ amino acids F. Large molecules that hold genetic information __D___ monosaccharides G. Forms body structures (hair, skin, muscle, bone) and enzymes __I___ ATP H. The process in which an egg and a sperm join __L____ enzyme I. The energy source that cells can use __N____ denaturing J. Causes enzyme-catalyzed reactions to slow down K. The process of breaking down glucose to make ATP __M___ zygote L. A molecule that speeds up chemical reactions __H___ fertilization M. A fertilized egg cell that will develop into an embryo N. The process in which an enzyme loses its structure (and can no longer work) due to high heat or extreme pH ___F___ nucleic acids __G____ proteins __B___ carbohydrates 3. More matching! __K___ cell respiration __J___ cold temperatures Key Terms and Content Review for Today’s Class Term prokaryote What Kind of Organisms It’s In Bacteria nucleus Description A cell with no nucleus or other membrane-enclosed organelles. Small and simple. A cell with a nucleus and other membrane-enclosed organelles. Larger and more complex. Holds and protects DNA cytoplasm The fluid that fills cells all ribosome Makes proteins all lysosome Contains digestive enzymes eukaryotes cell membrane all mitochondrion Controls what enters and leaves the cell Performs cellular respiration chloroplast Perform photosynthesis plants, some protists ER Modifies and transports proteins eukaryotes Golgi Packages proteins eukaryotes mitochondrion Makes ATP eukaryotes cell membrane Made of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins Provides sturdy structure around the outside of the cell Spreading out of materials from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Diffusion of water across a membrane Movement of materials from low concentration to high concentration; requires energy! all eukaryote cell wall diffusion osmosis active transport Word Bank (two of the words are used twice): Mitochondria Cell membrane Cell wall Lysosome Cytoplasm Golgi apparatus Endoplasmic reticulum Nucleus plants, animals, fungi, protists eukaryotes eukaryotes plants, fungi, bacteria Prokaryote Eukaryote Chloroplast Ribosome Osmosis Active transport Diffusion Practice Problems: 1. 5. Explain: Explain: 2. 6. Explain: 3. 7. Explain: 4. 8. Explain: 9. 10. Explain: Cell walls and chloroplasts 11. Cell Explain: Cell X has no nucleus and is smaller, Cell Y has a nucleus and is bigger Explain: 12. 15. Explain: Using energy and going from low to high conc. 13. 16. Explain: 14. 17. Explain: 18. 19. Explain: Structure 3 is a vacuole that stores water, etc. Explain: Prokaryotes have DNA not in a nucleus