Cell Chart Review
advertisement

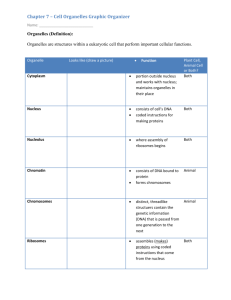
Cell Chart Review •“little organs” •each one performs a specialized function that enables the cells to survive. •found only inside eukaryotic cells Embryonic Stem Cells Eukaryotic cells, found in animals. In early development these cells have the potential to become any cell in the body. Currently stem cells can be harvested from embryos, cord blood, and now some adult cells can be induced to turn back the clock and become stem cells. Stem cell research may hold the answer to many questions about human health and disease. It can be controversial due to the harvesting of cells from human embryos. Cell Membrane Regulates what goes in and out of the cell “doorman” Selectively permeable Fluid-mosaic model of the cell membrane Proteins Cell Wall protects the PLANT cell and maintains its shape located outside of the cell membrane made of cellulose in plants NOTE: prokaryotes and fungi have a cell wall too! Cytoplasm suspends organelles “jelly-like” Nucleolus Makes ribosomes Located inside the nucleus Nucleus, DNA, Nuclear Membrane (NM) Nucleus: houses the cell's genetic material in the form of DNA; controls reproduction and metabolism “brain” DNA: Gentic material NM: surrounds nucleus, contains pores Ribosomes Make proteins Endoplasmic Reticulum (E.R.) Can be Rough or Smooth Rough E.R.: contains ribosomes; a system of tubes and sacs that transport these proteins “highway” Smooth E.R. No ribosomes builds lipid molecules also detoxifies the cell of poisons or toxins, including drugs or medicine. Golgi Apparatus and Vesicles Golgi Apparatus: modifies, stores, and packages proteins and other chemical products to their next destinations processing and shipping center “UPS” Products are “shipped” in vesicles Vesicles (bottom of cell chart) “shipping containers” move products (proteins, water, waste) into, out of, and within a cell Organelles work together… Vacuoles Central Vacuole in Plants - stores water and salts, causes cells to expand Animals - stores undigested nutrients Paramecium – Contractile Vacuole pump out excess water that diffuses into the cell Lysosomes Contain digestive enzymes that break down wastes or expose food “garbage disposal” help destroy harmful bacteria “suicide sacs” Recycle damaged organelles “recycling center” Tadpoles loose their tails when the lysosomes open at the base of their bodies Organelles work together… Chloroplasts - capture sunlight and transforms it into carbohydrates (glucose) - photosynthesis - contains green pigment chlorophyll Mitochondria “Powerhouse” – make energy Cellular respiration occurs here to release energy for the cell to use Cytoskeleton maintains cell shape and protects the cell Cilia and Flagella Cilia: short hair-like extensions Flagella:long tail-like extenstions Both aid in movement Cilia in our Lungs Centrioles Animal cells only Paired structures Move chromosomes during cell division