Here is a PowerPoint designed to help you review the parts of a cell.
advertisement

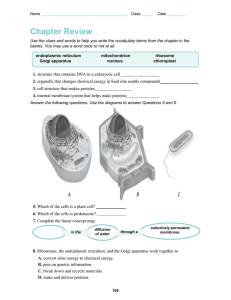
The Parts of a Cell Illustrations reproduced from Florida State University http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/animalcell.html 1. Found only in plant cells. 2. Photosynthesis occurs within this structure. 3. Contains chlorophyll, a green pigment active in photosynthesis. The Chloroplast 1. Releases the energy needed for the cell’s survival. 2. In order to produce this energy, this structure breaks down glucose in a process called RESPIRATION. 3. Often called the “powerhouse of the cell”. The Mitochondria 1. Series of passageways that extends from the nucleus through the cytoplasm. 2. Produces small vesicles which are used to transport materials, such as proteins, to the Golgi Bodies and the rest of the cell. 3. Found in two forms: Smooth and Rough The Endoplasmic Reticulum 1. Controls all the activities of the cell, including cellular reproduction. 2. Contains the cell’s chromatin (DNA). 3. Called the “control center” of the cell. The Nucleus 1. Considered to be the distribution and shipping department for the cell’s chemical products. 2. May modify the proteins and lipids (fats) that have been shipped from the ER and prepare them for export outside of the cell or for transport to other locations in the cell. The Golgi Body 1. Found only in plant cells. 2. Protects the plant cell. 3. This rigid structure, made of cellulose, gives shape to the plant cell. 4. The only non-living part of the cell. The Cell Wall 1. Found in both plant and animal cells. 2. Serves as storage for water, food and waste 3. Largest organelle found in plant cells The Vacuole 1. Responsible for the production of proteins in the cell. 2. Found either attached to the walls of the endoplasmic reticulum or floating freely in the cytoplasm. The Ribosome 1. Found primarily in animal cells 2. This is the site where materials are broken down or recycled in the cell. 3. These structures contain proteins called enzymes which are responsible for breaking down materials. The Lysosome 1. Found in both plant and animal cells. 2. Forms the outside boundary of animal cells. 3. Responsible for controlling what materials enter and exit from the cell. 4. Flexible The Cell Membrane