Plant & Animal Cells: Vocabulary & Definitions
advertisement

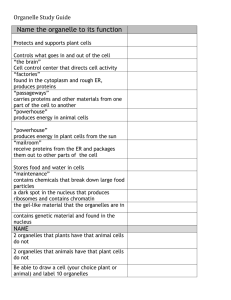
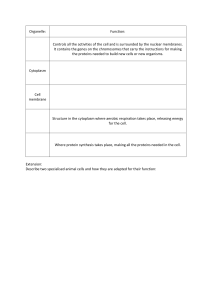
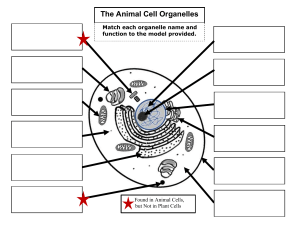
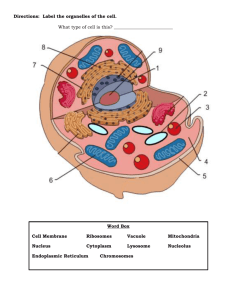
Plant and Animal Cells Word Bank Organelle – the structure in plant and animal cells that perform specific functions Cytoplasm – a clear, jellylike substance that holds the organelles in place Chloroplasts – organelles, found only in plant cells, in which sugar is made during photosynthesis Photosynthesis – is the process in which plant cells convert water and carbon dioxide in the presence of sunlight to sugar and water, releasing oxygen Cell Membrane – A protective layer surrounding the cell that controls what enters and leaves the cell. (both plant and animal cell have this) Cell wall – a stiff outer layer that surrounds a plant cell, protects it, and gives it its shape Nucleus – the control center of a cell that directs the cell’s activities Chromosomes – structures in the nucleus that contain an organism’s genetic information and regulate the cell’s activities DNA – the abbreviation for deoxyribonucleic acid, the chemical that provides detailed instructions for cells Mitochondria – a bean shaped organelle that goes through a process which releases energy in order for the cell to complete all its activities Vacuole – a storage place for nutrients, wastes, and water. A plant cell has a much larger vacuole than an animal cell because it stores more water and sugars Ribosome – small organelles located in the nucleus where proteins are constructed Lysosome – small round structures located in the cytoplasm that are responsible for breaking down large food particles into smaller substances needed for cell function Endoplasmic Reticulum – passage ways in the cytoplasm that transport proteins throughout the cell