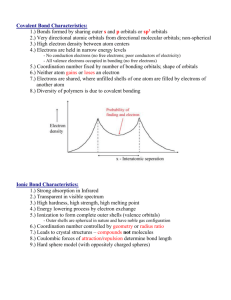
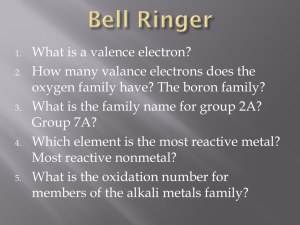History of Atom
advertisement
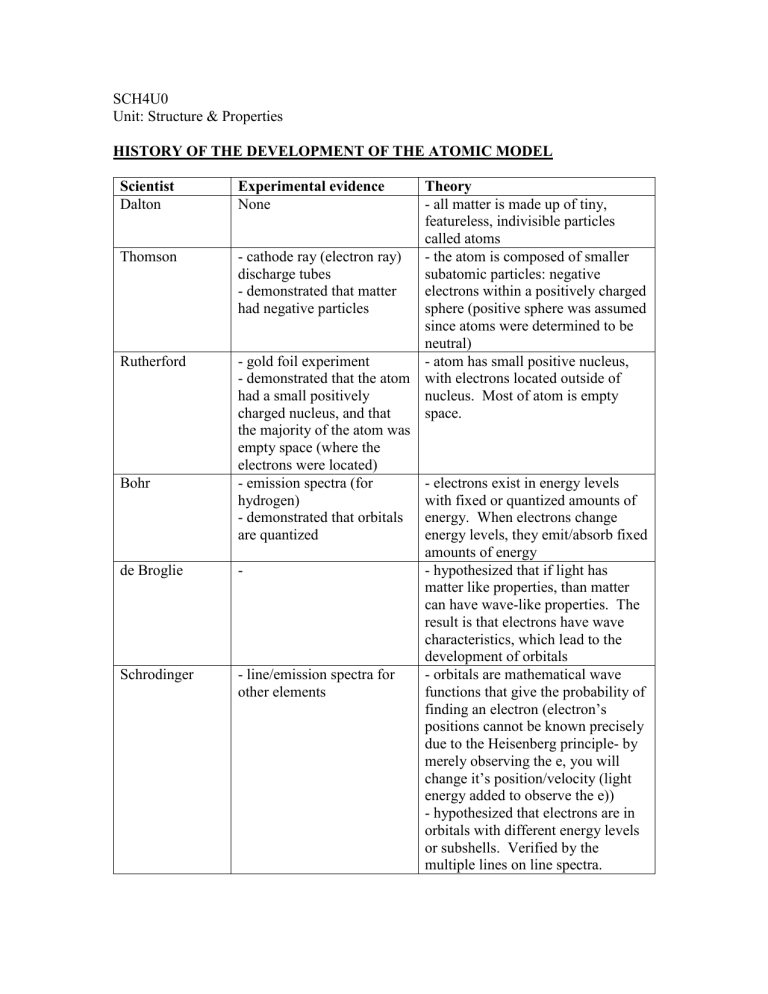
SCH4U0 Unit: Structure & Properties HISTORY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE ATOMIC MODEL Scientist Dalton Thomson Rutherford Bohr de Broglie Schrodinger Experimental evidence None Theory - all matter is made up of tiny, featureless, indivisible particles called atoms - cathode ray (electron ray) - the atom is composed of smaller discharge tubes subatomic particles: negative - demonstrated that matter electrons within a positively charged had negative particles sphere (positive sphere was assumed since atoms were determined to be neutral) - gold foil experiment - atom has small positive nucleus, - demonstrated that the atom with electrons located outside of had a small positively nucleus. Most of atom is empty charged nucleus, and that space. the majority of the atom was empty space (where the electrons were located) - emission spectra (for - electrons exist in energy levels hydrogen) with fixed or quantized amounts of - demonstrated that orbitals energy. When electrons change are quantized energy levels, they emit/absorb fixed amounts of energy - hypothesized that if light has matter like properties, than matter can have wave-like properties. The result is that electrons have wave characteristics, which lead to the development of orbitals - line/emission spectra for - orbitals are mathematical wave other elements functions that give the probability of finding an electron (electron’s positions cannot be known precisely due to the Heisenberg principle- by merely observing the e, you will change it’s position/velocity (light energy added to observe the e)) - hypothesized that electrons are in orbitals with different energy levels or subshells. Verified by the multiple lines on line spectra.