Ionic Bond Characteristics:
advertisement
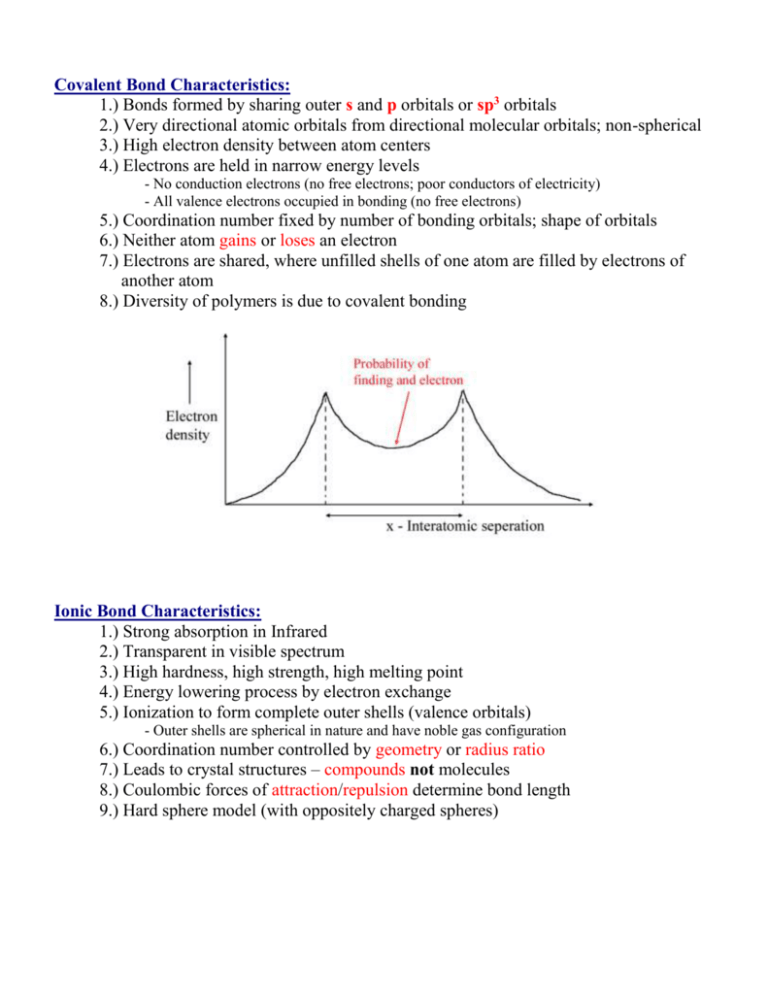
Covalent Bond Characteristics: 1.) Bonds formed by sharing outer s and p orbitals or sp3 orbitals 2.) Very directional atomic orbitals from directional molecular orbitals; non-spherical 3.) High electron density between atom centers 4.) Electrons are held in narrow energy levels - No conduction electrons (no free electrons; poor conductors of electricity) - All valence electrons occupied in bonding (no free electrons) 5.) Coordination number fixed by number of bonding orbitals; shape of orbitals 6.) Neither atom gains or loses an electron 7.) Electrons are shared, where unfilled shells of one atom are filled by electrons of another atom 8.) Diversity of polymers is due to covalent bonding Ionic Bond Characteristics: 1.) Strong absorption in Infrared 2.) Transparent in visible spectrum 3.) High hardness, high strength, high melting point 4.) Energy lowering process by electron exchange 5.) Ionization to form complete outer shells (valence orbitals) - Outer shells are spherical in nature and have noble gas configuration 6.) Coordination number controlled by geometry or radius ratio 7.) Leads to crystal structures – compounds not molecules 8.) Coulombic forces of attraction/repulsion determine bond length 9.) Hard sphere model (with oppositely charged spheres)