Catalase Intro Lab
advertisement

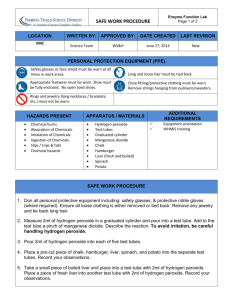
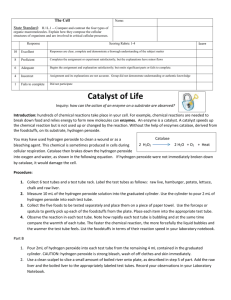
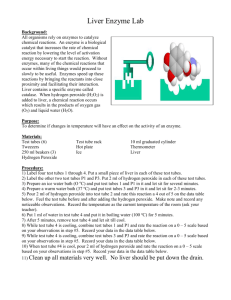
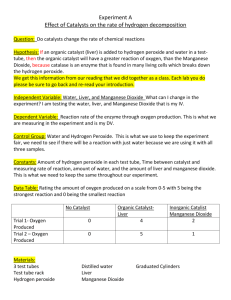
Name: ________________________________________________________________ Date: _____________________ Introduction to Enzymes Lab Period: ___________________ Introduction: In each individual cell of a human there are many chemical reactions taking place, performing the necessary functions for being a large, complex, multicellular organism. Enzymes are biological catalysts. They help to increase the rate of chemical reactions. Enzymes are most often proteins and their three-dimensional shape is important to their catalytic activity. Because of their 3-D shape, enzymes are highly specific for the reactions that they catalyze. In other words, they are highly specific for the substrates that they will act upon. So any one "function", such as getting energy from a glucose molecule, actually involves many reactions, each with a specific enzyme. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a highly active chemical, often used for bleaching; it is sold as a 3% solution in water. Within cells hydrogen peroxide is thought to be formed continually as a by-product of biochemical processes. Because it is toxic, or poisonous, it would soon kill cells if not removed or broken down immediately. The chemical formula for this reaction is: Catalase 2H2O2 2H2O + O2 Procedure: Test tube 1 Distilled water 1. 2. 3. 4. Smash a piece of liver in a mortar and pestle Place 2 mL of distilled water in a test tube. Add a small piece of liver. Note reaction in table. Test tube 2 – Part A 3% hydrogen peroxide 1. 2. 3. 4. Smash a piece of liver in a mortar and pestle Place 2 mL of hydrogen peroxide in a test tube. Add a small piece of liver. Note reaction in table. Test tube 2 – Part B 3% hydrogen peroxide 1. Pour out hydrogen peroxide but leave the liver from test tube 2. 2. Place 2 mL of hydrogen peroxide in a test tube. 3. Note reaction in table Note the extent of the reaction (No bubbles, a few bubbles, lots of bubbles) Test tube # Extent of reaction Test tube 1 Test tube 2 – part A Test tube 2 – part B Questions: 1. Does the liver have a catalyst that reacts with peroxide? __________________________________. 2. What is the name of the catalyst found in the liver? __________________________________. 3. What is the substrate? __________________________________. 4. What are the products? __________________________________. 5. What are the bubbles? __________________________________. 6. What is the purpose of test tube 1? ___________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. What is the purpose of test tube 2 part b? ____________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Look at your results for the liver and hydrogen peroxide reaction. Assuming the reaction is complete, what is this liquid composed of? What do you think would happen if you added more liver to this liquid? _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. What cells in our bodies contain catalase? Why? _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________