Liver Enzyme Lab
advertisement

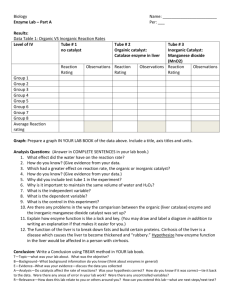
Name __________________________________ Period _______ Date ______________ Liver Enzyme Lab *Important Vocabulary: Define the terms listed below. Reactants: Products: Enzyme: Substrate: Catalase: H202: chemical formula for hydrogen peroxide *The chemical reaction to be tested in this experiment is explained in words and chemical symbols below: Words: Hydrogen peroxide in the presence of the proper enzyme goes to form oxygen plus H2O. Chemical Symbols: 2 H2O2 ---enzyme-- O2 + 2 H20 2 hydrogen peroxides oxygen 2 waters *Background Info: What is the substrate in the above reaction? _____________________________________________ What is the reactant? _______________________________________________________________ What is the name of the enzyme? _____________________________________________________ Name the two products in the reaction. _________________________________________________ *More Background Info: >When hydrogen peroxide is broken down by catalase, bubbles of oxygen gas are released. >The faster the reaction, the thicker the layer of bubbles. >We will use a 6-point scale to measure the reaction rate: 0 = No bubbles 1 = Slight bubble formation 2 = Bubbles rise ¼ up the test tube 3 = Bubbles rise ½ up the test tube 4 = Bubbles rise ¾ up the test tube 5 = Bubbles reach the top of the test tube 6 = Bubbles flow over the top of the test tube >CAUTION!! When the reaction occurs, the bubbles may lift the piece of liver you are testing up and out of the hydrogen peroxide in the test tube. Use the glass rod to hold the liver down during the reaction. Remove the rod when the reaction looks like it’s done and record the rate. EXPERIMENT #1 – CATALASE RXN: Observe the enzyme, catalase, reacting in liver cells. PROCEDURE: 1. Place 2 mL of hydrogen peroxide in one test tube. 2. Get a piece of liver (the size of a pea) and place it in the test tube. 3. Observe what happens and record the reaction rate. (Make sure the liver stays at the bottom…use the glass rod to push it down) RESULTS: Liver Reaction Rate: ________ CONCLUSION: What causes the liver to float upwards? What assumptions can you make about the level of activity of the enzyme and how fast bubbles are produced? EXPERIMENT #2 – EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE: Will high temperature have an effect on enzyme activity? PROCEDURE: 1. Place a piece of liver in a test tube. 2. Take the test tube over to the hot water bath and place it in the bath for 5 minutes. KEEP TRACK OF TIME! 3. After 5 minutes, remove the test tube from the bath and place it in your test tube rack to cool. 4. After it has cooled, add 2mL of fresh hydrogen peroxide to the test tube 5. Observe and record the record the reaction rate. 6. Compare the reaction rate for this experiment to the reaction rate from experiment #1. RESULTS: Liver Reaction Rate from Experiment #1: ________ Liver Reaction Rate from Experiment #2: ________ CONCLUSION: Did the heat slow down the action of the enzyme? Knowing that enzymes are folded proteins with specific shapes, explain what you think heat did to them.