Enzyme Answers lab A
advertisement

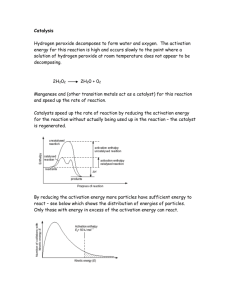
Experiment A Effect of Catalysts on the rate of hydrogen decomposition Question: Do catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions Hypothesis: If an organic catalyst (liver) is added to hydrogen peroxide and water in a testtube, then the organic catalyst will have a greater reaction of oxygen, than the Manganese Dioxide, because catalase is an enzyme that is found in many living cells which breaks down the hydrogen peroxide. We get this information from our reading that we did together as a class. Each lab you do please be sure to go back and re-read your introduction. Independent Variable: Water, Liver, and Manganese Dioxide What can I change in the experiment? I am testing the water, liver, and Manganese Dioxide that is my IV. Dependent Variable: Reaction rate of the enzyme through oxygen production. This is what we are measuring in the experiment and is my DV. Control Group: Water and Hydrogen Peroxide. This is what we use to keep the experiment fair, we need to see if there will be a reaction with just water because we are using it with all three samples. Constants: Amount of hydrogen peroxide in each test tube, Time between catalyst and measuring rate of reaction, amount of water, and the amount of liver and manganese dioxide. This is what we need to keep the same throughout our experiment. Data Table: Rating the amount of oxygen produced on a scale from 0-5 with 5 being the strongest reaction and 0 being the smallest reaction No Catalyst Trial 1- Oxygen Produced Trial 2 – Oxygen Produced Materials: 3 test tubes Test tube rack Hydrogen peroxide 0 Organic CatalystLiver 4 0 Distilled water Liver Manganese Dioxide Inorganic Catylist Manganese Dioxide 2 5 Graduated Cylinders 1 Procedure: 1. Wear goggles 2. Test one test tube at a time 3. Prepare contents as outlined below a. Test Tube 1 – 10mL water and 10mL of hydrogen peroxide b. Test Tube 2 – 10 mL water and 10 mL of H2O2 and small piece of liver c. Test Tube 3 – 10mL water and 10mL of H2O2 and pea size amount of MnO2 4. Record your observations and rate them in your table from 0-5 5. Clean up your lab 6. Create a graph of your results Graph: Effect of catalyst on a chemical reaction 6 5 4 Column1 3 Column2 Column3 2 1 0 H2o2 / H2o H2o2/Liver H2o2/MnO2 Conclusion using the CER method: C – Claim- According to the hypothesis, the liver had the greatest reaction to oxygen because it produced the most bubbles. The enzyme catalase speeds up the reaction rate which breaks down hydrogen peroxide, a toxic chemical into 2 harmless substances, which are water and oxygen. E – Evidence – Our graph above shows that liver had the greatest reaction compared to Manganese Dioxide and water in each of the 3 trials. Liver had a 4, 4.4, and 5.0 reaction rate while MnO2 had a 3.5, 3, and 2 reaction rate. Water and H2O2 had a zero reaction rate. R – Reason – The data collected in our lab connects with what happens in the human body. In each of our cells there are many chemical reactions that are taking place. Molecules are constantly forming bonds and breaking bonds. Enzymes are proteins that help support these processes. In this lab the enzyme Catalase speeds up this reaction which breaks down the hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. This is what formed the bubbles and how we measured our experiment.