Enzyme Lab: Amylase & Catalase Activity
advertisement

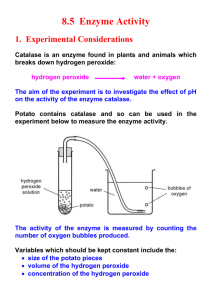
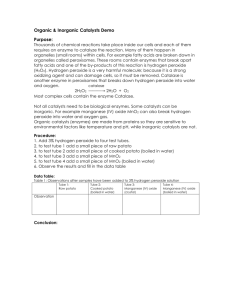
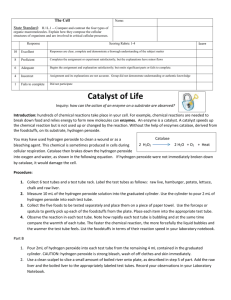
Enzyme Lab Biology Purpose: To demonstrate the effects of enzymes on biomolecules. Part 1. Effect of amylase in breaking down starchy or carbohydrate rich foods. 1. Crush a small part of a saltine cracker into a fine power, about 1/10 of a cracker. (This imitates the effects of mechanical digestion, chewing) 2. Place the crushed cracker in the bottom of a test tube, only enough to cover the bottom. 3. Add an equal amount of water to the test tube and mix thoroughly. cracker amount add an equal amount of water. 4. Add one drop of iodine (Lugol’s Solution) and mix thoroughly by gently swirling or rotating the test tube. Iodine is an indicator of a starch and will turn a blue-black when starch is present. What color is the iodine? What color change did you notice when the iodine was added to the cracker and water? The cracker would be an example of what Carbohydrate? 5. Double (or slightly more) the total volume in the test tube with saliva by letting some spit accumulate in your mouth and then spitting into the test tube. 6. Mix and wait about five minutes. Describe any changes. 7. Spit contains the enzyme amylase. Explain why the amylase caused changes to the crackeriodine mixture. 8. What does the starch break down into? 9. Below is a molecule of lactose (substrate). Draw the shape of the enzyme that would be necessary to break apart this substrate. Label the enzyme and the active site of the enzyme. Show the substrate products that resulted from the breakdown of lactose. Part 2: Catalase and the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide Catalase is an enzyme that decomposes molecules of hydrogen peroxide which is a chemical produced by some chemical reaction in cells. Catalase like all enzyme is specific for one job. This means that catalase can only decompose one chemical, which is hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide must be removed or it could destroy the cell. But hydrogen peroxide also kills bacteria and aids in the repair of nerves when your skin is cut. Decomposition of hydrogen peroxide: 2H2O2 2H2O + O2 1. Cut a small piece of potato and place in a test tube. Draw your test tube with the potato. Label 2. Add 10-15 drops of hydrogen peroxide. Describe the reaction. 3. Using the equation above, explain what the drops of hydrogen peroxide are being changed into. What is the evidence of oxygen being released? What is the liquid remaining in the test tube with the potato?