Catalysts of Life lab
advertisement

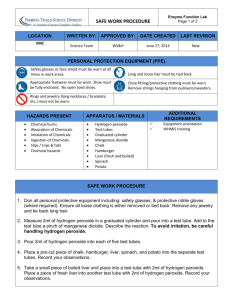
The Cell Name: State Standard: H.1L.1 -- Compare and contrast the four types of organic macromolecules. Explain how they compose the cellular structures of organisms and are involved in critical cellular processes. Response Scoring Rubric 1-4 10 Excellent Responses are clear, complete and demonstrate a thorough understanding of the subject matter 8 Proficient Completes the assignment or experiment satisfactorily, but the explanations have minor flaws 6 Adequate Begins the assignment and explanation satisfactorily; but omits significant parts or fails to complete. 4 Incorrect Assignment and its explanations are not accurate. Group did not demonstrate understanding or authentic knowledge 1 Fails to complete Did not participate Score Catalyst of Life Inquiry: how can the action of an enzyme on a substrate are observed? Introduction: hundreds of chemical reactions take place in your cell. For example, chemical reactions are needed to break down food and relies energy to form new molecules can enzymes. An enzyme is a catalyst. A catalyst speeds up the chemical reaction but is not used up or changed by the reaction. Without the help of enzymes catalase, derived from the foodstuffs, on its substrate, hydrogen peroxide. Catalase You may have used hydrogen peroxide to clean a wound or as a 2 H2O2 e 2 H2O + O2 + Heat bleaching agent. This chemical is sometimes produced in cells during cellular respiration. Catalase then brakes down the hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water, as shown in the following equation. If hydrogen peroxide were not immediately broken down by catalase, it would damage the cell. Procedure: 1. Collect 6 test tubes and a test tube rack. Label the test tubes as follows: raw live, hamburger, potato, lettuce, chalk and raw liver. 2. Measure 10 mL of the hydrogen peroxide solution into the graduated cylinder. Use the cylinder to pour 2 mL of hydrogen peroxide into each test tube. 3. Collect the five foods to be tested separately and place them on a piece of paper towel. Use the forceps or spatula to gently pick up each of the foodstuffs from the plate. Place each item into the appropriate test tube. 4. Observe the reaction in each test tube. Note how rapidly each test tube is bubbling and at the same time compare the warmth of each tube. The faster the chemical reaction, the more forcefully the liquid bubbles and the warmer the test tube feels. List the foodstuffs in terms of their reaction speed in your laboratory notebook. Part B 1. Pour 2mL of hydrogen peroxide into each test tube from the remaining 4 mL contained in the graduated cylinder. CAUTION: hydrogen peroxide is strong bleach, wash of off clothes and skin immediately. 2. Use a clean scalpel to slice a small amount of boiled river onto plate, as described in step 5 of part. Add the raw liver and the boiled liver to the appropriately labeled test tubes. Record your observations in your Laboratory Notebook. Laboratory Notebook Catalyst of Life Hypothesis: ___________________________________________________________________________ Enzyme Sources Fast Reaction Slow Reaction 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Data Record: Description of Liver reactions Raw Liver Boiled Liver Conclusion 1. EVALUATE your hypothesis. What evidence do you have that supports or rejects it? if your hypothesis was incorrect, how could you RESTATE it? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 2. EXPLAIN why the test tubes felt warm. ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. IDENTIFY which of the substances that you tested in part A contained the most catalase? __________________ 4. Did any of the substances not produce a reaction? EXPLAIN why or why not? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 5. What might you HYPOTHESIZE about the amount of catalase in animals and plants ___________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 6. What can you INFER about the effect of boiling enzymes, based on your observation in part B? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ A Step Further (EXTRA CREDIT BIG POINTS) see me. Design and experiment that tests the effect of freezing on the activity of catalase. You might also test catalase activity using other sources of animal cells and plant cells and compare your observations.